Risk factors for mortality of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33593433
- PMCID: PMC7885396
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-021-02435-9
Risk factors for mortality of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH) is a rare but life-threatening complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The current knowledge of the prognostic factors for SLE-associated DAH is controversial. This meta-analysis was undertaken to investigate the relevant risk factors for mortality in SLE-associated DAH.
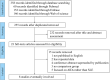
Methods: Studies were searched from PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science databases published up to May 27, 2020, and were selected or removed according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Two reviewers extracted data independently from the enrolled studies, and the odds ratios (OR) or the standardized mean difference (SMD) was utilized to identify and describe the prognostic factors for mortality.
Results: Eight studies encompassing 251 patients with SLE-associated DAH were included in the meta-analysis. No significant publication bias was shown. Age at the diagnosis of DAH (SMD = 0.35, 95% confidence interval (CI) (0.08, 0.61), P = 0.01, I2 = 0.0%) was found to be an independent risk factor of mortality. Longer lupus disease duration (SMD = 0.28, 95% CI (0.01, 0.55), P = 0.042, I2 = 0.0%), concurrent infection (OR = 2.77, 95% CI (1.55, 4.95), P = 0.001, I2 = 37.5%), plasmapheresis treatment (OR = 1.96, 95% CI (1.04, 3.70), P = 0.038, I2 = 14.6%), and mechanical ventilation (OR = 6.11, 95% CI (3.27, 11.39), P < 0.0001, I2 = 23.3%) were also related to poor survival, whereas no noticeable relationships were revealed between survival and concurrent lupus nephritis (OR = 5.45, 95% CI (0.52, 56.95), P = 0.16, I2 = 58.4%) or treatment of cyclophosphamide (CTX) (OR = 0.74, 95% CI (0.16, 3.41), P = 0.70, I2 = 75.5%).
Conclusions: Older age at the diagnosis of DAH, longer disease duration of SLE, concurrent infection, plasmapheresis treatment, and mechanical ventilation were found related to increased mortality in patients with SLE-associated DAH according to our meta-analysis. However, due to limited studies with heterogeneity, these results should be interpreted cautiously. Notably, severe diseases rendered the requirement of plasmapheresis treatment and mechanical ventilation are themselves associated with poor outcome. Randomized trials of therapeutics are needed to determine the most efficacious strategies for SLE-associated DAH for better management of this life-threatening complication.
Keywords: Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage; Mortality; Risk factors; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Mintz G, Galindo LF, Fernández-Diez J, Jiménez FJ, Robles-Saavedra E, Enríquez-Casillas RD. Acute massive pulmonary hemorrhage in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1978;5(1):39–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

