Current Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- PMID: 33593479
- PMCID: PMC8021971
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2020.0843
Current Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Abstract
Background: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is characterized by the occurrence of.disorders of urine storage and bladder emptying. Most men over the age of 60 years are affected to some degree.
Methods: A selective literature search with additional scrutiny of guidelines and meta-analyses.
Results: The management of patients with BPH is complex. Emptying and retention disorders can be treated by various pharmacological and surgical means. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) has long been considered the gold standard for operative treatment. Transurethral enucleation procedures show a better risk profile in some uses, however, and have, above all, largely displaced suprapubic prostatectomy. Numerous innovative treatment options have been developed in recent years, but their long-term effects remain to be determined. These treatment techniques can nevertheless be used in individual cases after thorough discussion with the patient.
Conclusion: The care of patients with BPH should be interdisciplinary. The efficacy and safety of many new developments in the area of pharmacological and minimally invasive treatment remain to be demonstrated in randomized trials.
Figures
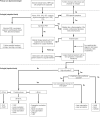
References
-
- Gravas S, Cornu J, Gacci M, et al. EAU Guidelines on management of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), incl benign prostatic obstruction (BPO) 2019. European Association of Urology 2019. https://uroweb.org/guideline/treatment-of-non-neurogenic-male-luts/ (last accesssed on 19 September 2019)
-
- Barry MJ, Fowler FJ Jr, O‘Leary MP, et al. The American Urological Association symptom index for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Measurement Committee of the American Urological Association. J Urol. 1992;148:1549–1564. - PubMed
-
- Egan KB. The epidemiology of benign prostatic hyperplasia associated with lower urinary tract symptoms: prevalence and incident rates. Urol Clin North Am. 2016;43:289–297. - PubMed
-
- Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol. 1984;132:474–479. - PubMed
-
- Vuichoud C, Loughlin KR. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: epidemiology, economics and evaluation. Can J Urol. 2015;22:1–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

