Antifungal activity of Acylhydrazone derivatives against Sporothrix spp
- PMID: 33593845
- PMCID: PMC8092869
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02593-20
Antifungal activity of Acylhydrazone derivatives against Sporothrix spp
Abstract
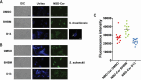
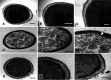
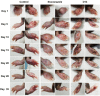
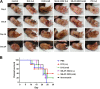
Sporotrichosis is an emerging mycosis caused by members of the genus Sporothrix The disease affects humans and animals, particularly cats, which plays an important role in the zoonotic transmission. Feline sporotrichosis treatment options include itraconazole (ITC), potassium iodide and amphotericin B, drugs usually associated with deleterious adverse reactions and refractoriness in cats, especially when using ITC. Thus, affordable, non-toxic and clinically effective anti-Sporothrix agents are needed. Recently, acylhydrazones (AH), molecules targeting vesicular transport and cell cycle progression, exhibited a potent antifungal activity against several fungal species and displayed low toxicity when compared to the current drugs. In this work, the AH derivatives D13 and SB-AF-1002 were tested against Sporothrix schenckii and Sporothrix brasiliensis Minimal inhibitory concentrations of 0.12 - 1 μg/mL were observed for both species in vitro D13 and SB-AF-1002 showed an additive effect with itraconazole. Treatment with D13 promoted yeast disruption with release of intracellular components, as confirmed by transmission electron microscopy of S. brasiliensis exposed to the AH derivatives. AH-treated cells displayed thickening of the cell wall, discontinuity of the cell membrane and an intense cytoplasmic degeneration. In a murine model of sporotrichosis, treatment with AH derivatives was more efficient than ITC, the drug of choice for sporotrichosis. The results of the preliminary clinical study in cats indicate that D13 is safe and has potential to become a therapeutic option for sporotrichosis when associated to ITC. Our results expand the antifungal broadness of AH derivatives and suggest that these drugs could be exploited to combat sporotrichosis.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Sizar O, Talati R. 2020. Sporotrichosis. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island, FL. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30335288/. - PubMed
-
- Almeida-Paes R, de Oliveira MM, Freitas DF, do Valle AC, Zancopé-Oliveira RM, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC. 2014. Sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Sporothrix brasiliensis is associated with atypical clinical presentations. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8:e3094. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003094. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

