Early life adversity promotes resilience to opioid addiction-related phenotypes in male rats and sex-specific transcriptional changes
- PMID: 33593913
- PMCID: PMC7923376
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2020173118
Early life adversity promotes resilience to opioid addiction-related phenotypes in male rats and sex-specific transcriptional changes
Erratum in
-
Correction for Ordoñes Sanchez et al., Early life adversity promotes resilience to opioid addiction-related phenotypes in male rats and sex-specific transcriptional changes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Apr 26;119(17):e2204210119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2204210119. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35452315 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
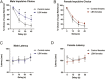
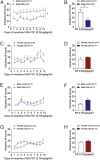
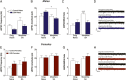
Experiencing some early life adversity can have an "inoculating" effect that promotes resilience in adulthood. However, the mechanisms underlying stress inoculation are unknown, and animal models are lacking. Here we used the limited bedding and nesting (LBN) model of adversity to evaluate stress inoculation of addiction-related phenotypes. In LBN, pups from postnatal days 2 to 9 and their dams were exposed to a low-resource environment. In adulthood, they were tested for addiction-like phenotypes and compared to rats raised in standard housing conditions. High levels of impulsivity are associated with substance abuse, but in males, LBN reduced impulsive choice compared to controls. LBN males also self-administered less morphine and had a lower breakpoint on a progressive ratio reinforcement schedule than controls. These effects of LBN on addiction-related behaviors were not found in females. Because the nucleus accumbens (NAc) mediates these behaviors, we tested whether LBN altered NAc physiology in drug-naïve and morphine-exposed rats. LBN reduced the frequency of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents in males, but a similar effect was not observed in females. Only in males did LBN prevent a morphine-induced increase in the AMPA/NMDA ratio. RNA sequencing was performed to delineate the molecular signature in the NAc associated with LBN-derived phenotypes. LBN produced sex-specific changes in transcription, including in genes related to glutamate transmission. Collectively, these studies reveal that LBN causes a male-specific stress inoculation effect against addiction-related phenotypes. Identifying factors that promote resilience to addiction may reveal novel treatment options for patients.
Keywords: nucleus accumbens; sex difference; stress; substance use disorder; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of early life adversity on male reproductive behavior and the medial preoptic area transcriptome.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022 May;47(6):1231-1239. doi: 10.1038/s41386-022-01282-9. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35102257 Free PMC article.
-
Early resource scarcity causes cortical astrocyte enlargement and sex-specific changes in the orbitofrontal cortex transcriptome in adult rats.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 2:2023.07.01.547315. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.01.547315. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Neurobiol Stress. 2024 Jan 15;29:100607. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100607. PMID: 37425737 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Early experience alters developmental trajectory of central oxytocin systems involved in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation in Long-Evans rats.Horm Behav. 2020 Nov;126:104822. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2020.104822. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Horm Behav. 2020. PMID: 32730760
-
Extinction training regulates neuroadaptive responses to withdrawal from chronic cocaine self-administration.Learn Mem. 2004 Sep-Oct;11(5):648-57. doi: 10.1101/lm.81404. Learn Mem. 2004. PMID: 15466321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative consequences of early-life adversity on substance use as mediated by corticotropin-releasing factor modulation of serotonin activity.Neurobiol Stress. 2018 Aug 7;9:29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2018.08.001. eCollection 2018 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2018. PMID: 30151419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perinatal Morphine Exposure Leads to Sex-Dependent Executive Function Deficits and Microglial Changes in Mice.eNeuro. 2022 Oct 17;9(5):ENEURO.0238-22.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0238-22.2022. Print 2022 Sep-Oct. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 36216505 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptional Analyses in the Nucleus Accumbens Identifies RGS2 as a Key Mediator of Depression-Related Behavior.Biol Psychiatry. 2022 Dec 15;92(12):942-951. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2022.06.030. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Biol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36075764 Free PMC article.
-
A Double Hit of Social and Economic Stress in Mice Precipitates Changes in Decision-Making Strategies.Biol Psychiatry. 2024 Jul 1;96(1):67-78. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.12.011. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Biol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38141911 Free PMC article.
-
Early-life adversity increases anxiety-like behavior and modifies synaptic protein expression in a region-specific manner.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Oct 19;16:1008556. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1008556. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36338879 Free PMC article.
-
Postpartum scarcity-adversity inflicts sex-specific cerebellar adaptations and reward behaviors in adolescence.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2023 Oct;231:173620. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2023.173620. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2023. PMID: 37625522 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

