Transiently structured head domains control intermediate filament assembly
- PMID: 33593918
- PMCID: PMC7923618
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2022121118
Transiently structured head domains control intermediate filament assembly
Abstract
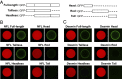
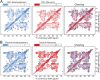
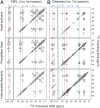
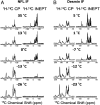
Low complexity (LC) head domains 92 and 108 residues in length are, respectively, required for assembly of neurofilament light (NFL) and desmin intermediate filaments (IFs). As studied in isolation, these IF head domains interconvert between states of conformational disorder and labile, β-strand-enriched polymers. Solid-state NMR (ss-NMR) spectroscopic studies of NFL and desmin head domain polymers reveal spectral patterns consistent with structural order. A combination of intein chemistry and segmental isotope labeling allowed preparation of fully assembled NFL and desmin IFs that could also be studied by ss-NMR. Assembled IFs revealed spectra overlapping with those observed for β-strand-enriched polymers formed from the isolated NFL and desmin head domains. Phosphorylation and disease-causing mutations reciprocally alter NFL and desmin head domain self-association yet commonly impede IF assembly. These observations show how facultative structural assembly of LC domains via labile, β-strand-enriched self-interactions may broadly influence cell morphology.
Keywords: in situ structural analysis; intermediate filaments; labile cross-β structures; low complexity domains; phase separation.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

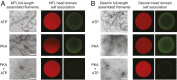
Comment in
-
Assembly of NFL and desmin intermediate filaments: Headed in the right direction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 30;118(13):e2102176118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2102176118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33707309 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Dynamic structural order of a low-complexity domain facilitates assembly of intermediate filaments.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 22;117(38):23510-23518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2010000117. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32907935 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of the desmin tail domain: studies using synthetic peptides and antipeptide antibodies.J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2063-75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2063. J Cell Biol. 1990. PMID: 2229186 Free PMC article.
-
αB-crystallin is a sensor for assembly intermediates and for the subunit topology of desmin intermediate filaments.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2017 Jul;22(4):613-626. doi: 10.1007/s12192-017-0788-7. Epub 2017 May 3. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2017. PMID: 28470624 Free PMC article.
-
Are the Head and Tail Domains of Intermediate Filaments Really Unstructured Regions?Genes (Basel). 2024 May 16;15(5):633. doi: 10.3390/genes15050633. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intermediate filaments and cellular mechanics.Cell Biol Int. 2018 Feb;42(2):132-138. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10879. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Cell Biol Int. 2018. PMID: 28980752 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: The wetware credentials of intermediate filaments involves coordinating, organising and networking in cells and tissues.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 13;11:1146618. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1146618. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36861037 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Type III intermediate filaments in redox interplay: key role of the conserved cysteine residue.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Apr 24;52(2):849-860. doi: 10.1042/BST20231059. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38451193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In situ architecture of a nucleoid-associated biomolecular co-condensate that regulates bacterial cell division.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jan 7;122(1):e2419610121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2419610121. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39739804 Free PMC article.
-
How do disordered head domains assist in the assembly of intermediate filaments?Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2023 Dec;85:102262. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2023.102262. Epub 2023 Oct 21. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37871501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Labile assembly of a tardigrade protein induces biostasis.Protein Sci. 2024 Apr;33(4):e4941. doi: 10.1002/pro.4941. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38501490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberts B., Molecular Biology of the Cell (Garland Science, New York, ed. 4, 2002).
-
- Patel S. S., Belmont B. J., Sante J. M., Rexach M. F., Natively unfolded nucleoporins gate protein diffusion across the nuclear pore complex. Cell 129, 83–96 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

