Effectiveness and safety of secukinumab in 608 patients with psoriatic arthritis in real life: a 24-month prospective, multicentre study
- PMID: 33593933
- PMCID: PMC7888309
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001519
Effectiveness and safety of secukinumab in 608 patients with psoriatic arthritis in real life: a 24-month prospective, multicentre study
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate in a multicentric Italian cohort of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) on secukinumab followed for 24 months: (1) the long-term effectiveness and safety of secukinumab, (2) the drug retention rate and minimal disease activity (MDA), (3) differences in the outcomes according to the biological treatment line: biologic-naïve patients (group A) versus multifailure (group B) patients.
Methods: Consecutive patients with PsA receiving secukinumab were evaluated prospectively. Disease characteristics, previous/ongoing treatments, comorbidities and follow-up duration were collected. Disease activity/functional/clinimetric scores and biochemical values were recorded at baseline (T0), 6(T6), 12(T12) and 24(T24) months. Effectiveness was evaluated overtime with descriptive statistics; multivariate Cox and logistic regression models were used to evaluate predictors of drug-discontinuation and MDA at T6. Infections and adverse events were recorded.
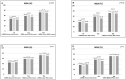
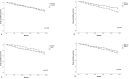
Results: 608 patients (41.28% men; mean (SD) age 52.78 (11.33)) were enrolled; secukinumab was prescribed as first-line biological treatment in 227 (37.34%) patients, as second (or more)-line biological treatment in 381 (62.66%). Effectiveness of secukinumab was shown with an improvement in several outcomes, such as Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (T0=3.26 (0.88) vs T24=1.60 (0.69) ;p=0.02) and Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (T0=25.29 (11.14) vs T24=7.69 (4.51); p<0.01). At T24, group A showed lower Psoriasis Area Severity Index (p=0.04), erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C reactive protein (p=0.03 ;p=0.05) and joint count (p=0.03) compared with group B. At T24, MDA was achieved in 75.71% of group A and 70.37% of group B. Treatment was discontinued in 123 (20.23%) patients, mainly due to primary/secondary loss of effectiveness, and in 22 due to adverse events. Retention rate at T24 was 71% in the whole population, with some difference depending on secukinumab dosage (p=0.004) and gender (p=0.05).
Conclusions: In a real-life clinical setting, secukimumab proved safe and effective in all PsA domains, with notable drug retention rate.
Keywords: antirheumatic agents; arthritis; biological therapy; psoriatic.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RR has received honoraria and speaker fees from Novartis, AbbVie, Pfizer, MSD, Janssen. AM has received honoraria and speaker fees from AbbVie, Pfizer, MSD, UCB, Novartis, Janssen, Eli-Lilly. LS speaker from Jansen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, MSD, Sanofi.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
