How Phagocytic Cells Kill Different Bacteria: a Quantitative Analysis Using Dictyostelium discoideum
- PMID: 33593980
- PMCID: PMC8545105
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.03169-20
How Phagocytic Cells Kill Different Bacteria: a Quantitative Analysis Using Dictyostelium discoideum
Abstract
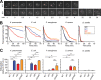
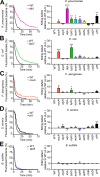
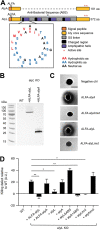
Ingestion and killing of bacteria by phagocytic cells protect the human body against infections. While many mechanisms have been proposed to account for bacterial killing in phagosomes, their relative importance, redundancy, and specificity remain unclear. In this study, we used the Dictyostelium discoideum amoeba as a model phagocyte and quantified the requirement of 11 individual gene products, including nine putative effectors, for the killing of bacteria. This analysis revealed that radically different mechanisms are required to kill Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtilis AlyL, a lysozyme-like protein equipped with a distinct bacteriolytic region, plays a specific role in the intracellular killing of K. pneumoniae, with assistance from BpiC and Aoah, two lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding proteins. Rapid killing of E. coli and P. aeruginosa requires the presence of BpiC and of the NoxA NADPH oxidase. No single effector tested is essential for rapid killing of S. aureus or B. subtilis Overall, our observations reveal an unsuspected degree of specificity in the elimination of bacteria in phagosomes.IMPORTANCE Phagocytic cells ingest and kill bacteria, a process essential for the defense of the human body against infections. Many potential killing mechanisms have been identified in phagocytic cells, including free radicals, toxic ions, enzymes, and permeabilizing peptides. Yet fundamental questions remain unanswered: what is the relative importance of these mechanisms, how redundant are they, and are different mechanisms used to kill different species of bacteria? We addressed these questions using Dictyostelium discoideum, a model phagocytic cell amenable to genetic manipulations and quantitative analysis. Our results reveal that vastly different mechanisms are required to kill different species of bacteria. This very high degree of specificity was unexpected and indicates that a lot remains to be discovered about how phagocytic cells eliminate bacteria.
Keywords: AlyL; Bacillus subtilis; Dictyostelium discoideum; Escherichia coli; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Staphylococcus aureus; killing; lysozyme.
Copyright © 2021 Jauslin et al.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
