A scalable physician-level deep learning algorithm detects universal trauma on pelvic radiographs
- PMID: 33594071
- PMCID: PMC7887334
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21311-3
A scalable physician-level deep learning algorithm detects universal trauma on pelvic radiographs
Abstract
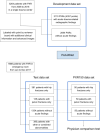
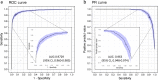
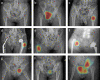
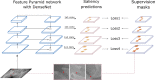
Pelvic radiograph (PXR) is essential for detecting proximal femur and pelvis injuries in trauma patients, which is also the key component for trauma survey. None of the currently available algorithms can accurately detect all kinds of trauma-related radiographic findings on PXRs. Here, we show a universal algorithm can detect most types of trauma-related radiographic findings on PXRs. We develop a multiscale deep learning algorithm called PelviXNet trained with 5204 PXRs with weakly supervised point annotation. PelviXNet yields an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.973 (95% CI, 0.960-0.983) and an area under the precision-recall curve (AUPRC) of 0.963 (95% CI, 0.948-0.974) in the clinical population test set of 1888 PXRs. The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity at the cutoff value are 0.924 (95% CI, 0.912-0.936), 0.908 (95% CI, 0.885-0.908), and 0.932 (95% CI, 0.919-0.946), respectively. PelviXNet demonstrates comparable performance with radiologists and orthopedics in detecting pelvic and hip fractures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

