MiR-543/Numb promotes proliferation, metastasis, and stem-like cell traits of prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 33594313
- PMCID: PMC7868851
MiR-543/Numb promotes proliferation, metastasis, and stem-like cell traits of prostate cancer cells
Abstract
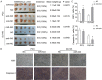
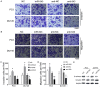
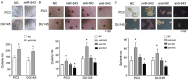
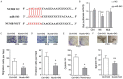
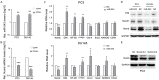
MiR-543 and Numb are associated with various malignancies, including prostate cancer (PCa). However, whether miR-543 regulates Numb in PCa development remains unclear. In this study, we identified Numb as a direct target of miR-543. The role of miR-543 was examined both in vitro and in vivo. The in vivo effects of miR-543 were investigated using tumor transplantation experiments and a lung metastasis model. The in vitro effects of miR-543 on proliferation, migration, invasion, and cancer stem-like cell (CSC)-associated properties were also examined. The binding sites of Numb were predicted using bioinformatics tools and confirmed by luciferase and rescue assays. QRT-PCR and western blot analyses were used to detect target expression levels. Expression levels of both miR-543 and Numb were manipulated in CD44+ and CD44-PCa cells followed by a series of functional assays. The results demonstrated that miR-543 promoted PCa growth and metastasis both in vivo and in vitro. Luciferase reporter assays, qRT-PCR, and western blot analyses revealed Numb as a direct target of miR-543. The function of miR-543 was abolished by Numb, as shown in rescue experiments. Moreover, miR-543 was verified to promote CSC properties, whereas Numb elicited the opposite effects. MiR-543 also influenced the expression of several stem-like factors, including Dll4, NF-κB, c-myc, and Oct-4, and the Numb/p53 signaling pathway. Taken together, these results demonstrate that miR-543 plays an oncogenic role by negatively controlling Numb, revealing the existence of an miR-543/Numb/p53 regulatory pathway in PCa tumorigenesis and development.
Keywords: CSC; Numb; miR-543; proliferation; prostate cancer.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
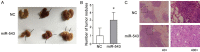

References
-
- Klemann N, Roder MA, Helgstrand JT, Brasso K, Toft BG, Vainer B, Iversen P. Risk of prostate cancer diagnosis and mortality in men with a benign initial transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy set: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:221–229. - PubMed
-
- Hellerstedt BA, Pienta KJ. The current state of hormonal therapy for prostate cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2002;52:154–179. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Luo X, Wu Y, Xia D, Chen W, Fang Z, Deng J, Hao Y, Yang X, Zhang T, Zhou L, Wu Y, Wang Q, Xu J, Hu X, Li L. MicroRNA-34a attenuates paclitaxel resistance in prostate cancer cells via direct suppression of JAG1/notch1 axis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50:261–276. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
