Berberine protects human and rat cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation-triggered apoptosis
- PMID: 33594316
- PMCID: PMC7868847
Berberine protects human and rat cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation-triggered apoptosis
Retraction in
-
Berberine protects human and rat cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation-triggered apoptosis [Retraction].Am J Transl Res. 2021 Dec 15;13(12):14241. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 35035773 Free PMC article.
Abstract
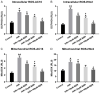
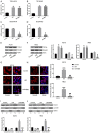
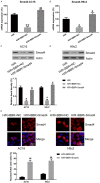
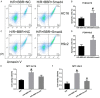
Berberine (BBR) confers potential cardioprotective effects. However, the relevant mechanisms underlying its regulation of cardiomyocyte survival following hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) treatment remain unknown. The present study investigated whether BBR could protect H/R by suppressing apoptosis and explored how TGF-β/Smad4 signaling pathway influenced H/R in vitro. Two cardiomyocyte cell lines-AC16 and H9c2- were treated with H/R and BBR. The survival and apoptosis of these two cell lines were assessed using the MTT and BrdU assays and western blotting (WB) and flow cytometry. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and caspase (Cas)-3, Cas-8, and Cas-9 activation were evaluated using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay as well as WB. Compared to the control group, H/R resulted in notable cell apoptosis, whereas BBR treatment evidently counteracted the process. BBR also markedly suppressed H/R-triggered excessive mitochondrial ROS generation and inhibited Smad4 expression. Overexpressing Smad4 in BBR-treated H/R-exposed cardiomyocytes reversed the effect of BBR treatment on apoptosis. Therefore, BBR protects H/R-treated cardiomyocytes from apoptosis by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad4 signaling pathway.
Keywords: BBR; TGF-β/smad4 pathway; apoptosis; cardiomyocytes; hypoxia/reoxygenation.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Saraste A, Pulkki K, Kallajoki M, Henriksen K, Parvinen M, Voipio-Pulkki LM. Apoptosis in human acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1997;95:320–323. - PubMed
-
- Kajstura J, Cheng W, Reiss K, Clark WA, Sonnenblick EH, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Olivetti G, Anversa P. Apoptotic and necrotic myocyte cell deaths are independent contributing variables of infarct size in rats. Lab Invest. 1996;74:86–107. - PubMed
-
- Remmers DE, Wang P, Cioffi WG, Bland KI, Chaudry IH. Testosterone receptor blockade after trauma-hemorrhage improves cardiac and hepatic functions in males. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:H2919–H2925. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
