POU2F1 induces the immune escape in lung cancer by up-regulating PD-L1
- PMID: 33594317
- PMCID: PMC7868838
POU2F1 induces the immune escape in lung cancer by up-regulating PD-L1
Abstract
Purpose: The aim was to research the POU2F1 related genes and mechanism during the progress of immune escape of lung cancer.
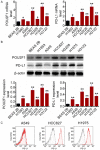
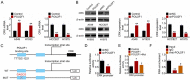
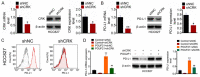
Methods: Lung cancer cell lines (H1993, HCC827, A549, H2228, H3122 and H1975) and Human normal lung epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B) were involved in this study. Overexpression or knockdown of POU2F1 was processed in lung cancer cells. POU2F1, PD-L1 and CRK expression in cells were detected by WB and RT-PCR. Flow cytometry and immunofluorescence was used to detect PD-L1 expression on the cell surface. Luciferase reporter detected the promoter activity of CRK. C57BL/6 mice models with knocked down of of POU2F1 were constructed. After tumor formation, anti-PD-1 was administered to detect tumor suppressing ability. IHC assay showed the number of intratumoral CD3+, CD8+, GranzB+ T cells.
Results: POU2F1 and PD-L1 were positively correlated in lung cancer cell lines. Overexpression of POU2F1 promoted the expression level of PD-L1 in lung cancer cells. POU2F1 transcription activated the expression of CRK, and further promoted the expression of PD-L1. Knockdown of POU2F1 promoted the efficacy of Anti-PD-1. In addition, tumor growth ability decreased after POU2F1 was knocked down. Cytotoxic effector cytokines levels, tumor suppressive chemokines and interleukin increased, while IL17a level decreased when POU2F1 was knocked down.
Conclusion: POU2F1 activates the expression of CRK, further promotes the expression of PD-L1, and finally improves the immune escape in lung cancer.
Keywords: Lung cancer; PD-L1; POU2F1; immune escape.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Disruption of SIRT7 Increases the Efficacy of Checkpoint Inhibitor via MEF2D Regulation of Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Gastroenterology. 2020 Feb;158(3):664-678.e24. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.025. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Gastroenterology. 2020. PMID: 31678303
-
LncRNA MALAT1 promotes tumorigenesis and immune escape of diffuse large B cell lymphoma by sponging miR-195.Life Sci. 2019 Aug 15;231:116335. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.040. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30898647
-
MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Regulates the Expression of Co-Stimulatory and Co-Inhibitory Molecules in Tumor Cells and Contributes to PD-L1-Mediated Suppression of Immune Cell Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 1;20(17):4287. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174287. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31480591 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA CHST15 Sponges miR-155-5p and miR-194-5p to Promote the Immune Escape of Lung Cancer Cells Mediated by PD-L1.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 11;11:595609. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.595609. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33777742 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody and EGFR-TKI on the expression of PD-L1 and function of T lymphocytes in EGFR-mutated lung cancer cells].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 23;38(12):886-892. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2016.12.002. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27998463 Chinese.
Cited by
-
CCT196969 inhibits TNBC by targeting the HDAC5/RXRA/ASNS axis to down-regulate asparagine synthesis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Aug 8;44(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03494-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40781327 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Characterization of Long Non-Coding RNA-Associated Networks to Reveal Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 27;11:720400. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.720400. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34513699 Free PMC article.
-
POU2F1 Promotes Cell Viability and Tumor Growth in Gastric Cancer through Transcriptional Activation of lncRNA TTC3-AS1.J Oncol. 2021 Jun 28;2021:5570088. doi: 10.1155/2021/5570088. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34257651 Free PMC article.
-
Further screening of SNP loci of eggshell translucency related genes and evaluation of genetic effects.Poult Sci. 2024 Sep;103(9):103963. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103963. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39013295 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of transcription factor POU2F1 confers improved survival on smokers with lung adenocarcinoma: a retrospective study of two cohorts.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Apr 28;12(4):727-741. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-714. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37197633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guo H, Deng Q, Wu C, Hu L, Wei S, Xu P, Kuang D, Liu L, Hu Z, Miao X. Variations in HSPA1B at 6p21.3 are associated with lung cancer risk and prognosis in chinese populations. Cancer Res. 2011;71:7576. - PubMed
-
- Qu CJ, Lin Y, Zhang HT. Hot spots in cancer immunotherapy and status quo of vaccine research for lung cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013;35:401–404. - PubMed
-
- Ding ZC, Lu XY, Yu M, Lemos H, Huang L, Chandler P, Liu K, Walters M, Krasinski A, Mack M, Blazar BR, Mellor AL, Munn DH, Zhou G. Immunosuppressive myeloid cells induced by chemotherapy attenuate antitumor cd4 t-cell responses through the PD-1-PD-L1 axis. Cancer Res. 2014;74:3441–3445. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
