Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and the Gastrointestinal Epithelium: Implications for the Gut-Brain Axis and Hypertension
- PMID: 33594519
- PMCID: PMC8364923
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-021-01044-z
Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and the Gastrointestinal Epithelium: Implications for the Gut-Brain Axis and Hypertension
Abstract
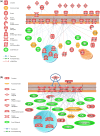
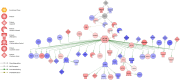
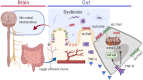
The colonic epithelium is the site of production and transport of many vasoactive metabolites and neurotransmitters that can modulate the immune system, affect cellular metabolism, and subsequently regulate blood pressure. As an important interface between the microbiome and its host, the colon can contribute to the development of hypertension. In this critical review, we highlight the role of colonic inflammation and microbial metabolites on the gut brain axis in the pathology of hypertension, with special emphasis on the interaction between tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and short chain fatty acid (SCFA) metabolites. Here, we review the current literature and identify novel pathways in the colonic epithelium related to hypertension. A network analysis on transcriptome data previously generated in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats reveals differences in several pathways associated with inflammation involving TNFα (NF-κB and STAT Expression Targets) as well as oxidative stress. We also identify down-regulation of networks associated with gastrointestinal function, cardiovascular function, enteric nervous system function, and cholinergic and adrenergic transmission. The analysis also uncovered transcriptome responses related to glycolysis, butyrate oxidation, and mitochondrial function, in addition to gut neuropeptides that serve as modulators of blood pressure and metabolic function. We present a model for the role of TNFα in regulating bacterial metabolite transport and neuropeptide signaling in the gastrointestinal system, highlighting the complexity of host-microbiota interactions in hypertension.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Butyrate; Gene networks; Hypertension; Inflammation; Microbiome.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal BB (2003) Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3:745–756. 10.1038/nri1184 - PubMed
-
- Ahmari N, Schmidt JT, Krane GA, Malphurs W, Cunningham BE, Owen JL, Martyniuk CM, Zubcevic J (2016) Loss of bone marrow adrenergic beta 1 and 2 receptors modifies transcriptional networks, reduces circulating inflammatory factors, and regulates blood pressure. Physiol Genomics 48(7):526–536. 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00039.2016 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andoh A, Fujiyama Y, Hata K, Araki Y, Takaya H, Shimada M, Bamba T (1999) Counter-regulatory effect of sodium butyrate on tumour necrosis factor- alpha (TNF-α)-induced complement C3 and factor B biosynthesis in human intestinal epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol 118(1):23–29. 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.01038.x - PMC - PubMed
-
- Areas MEZJ, Knapka J, Gleim G, Dipette D, Holland B, Preuss HG (1990) Influence of oat bran of sucrose-induced blood pressure elevations in SHR. Life Sci 47(13):1121–1128. 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90171-M - PubMed
-
- Arrieta MC, Stiemsma LT, Dimitriu PA, Thorson L, Russell S, Yurist-Doutsch S, Kuzeljevic B, Gold MJ, Britton HM, Lefebvre DL, Subbarao P (2015) Early infancy microbial and metabolic alterations affect risk of childhood asthma. Sci Transl Med 7(307):307ra152–307ra152. 10.1126/scitranslmed.aab2271 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

