Molecular response and quality of life in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with intermittent TKIs: First interim analysis of OPTkIMA study
- PMID: 33594821
- PMCID: PMC7940223
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3778
Molecular response and quality of life in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with intermittent TKIs: First interim analysis of OPTkIMA study
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Cancer Med. 2021 May;10(10):3486. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3922. Epub 2021 May 2. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33934555 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Intermittent treatment with TKIs is an option for the great majority (70%-80%) of CML patients who do not achieve a stable deep molecular response and are not eligible for treatment discontinuation. For these patients, the only alternative is to assume TKI continuously, lifelong.
Methods: The Italian phase III multicentric randomized OPTkIMA study started in 2015, with the aim to evaluate if a progressive de-escalation of TKIs (imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib) is able to maintain the molecular response (MR3.0 ) and to improve Health Related Quality of Life (HRQoL).
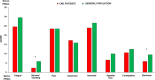
Results: Up to December 2018, 166/185 (90%) elderly CML patients in stable MR3.0 /MR4.0 completed the first year of any TKI intermittent schedule 1 month ON and 1 month OFF. The first year probability of maintaining the MR3.0 was 81% and 23.5% of the patients who lost the molecular response regained the MR3.0 after resuming TKI continuously. Patients' HRQoL at baseline was better than that of matched peers from healthy population. Women was the only factor independently associated with worse baseline HRQoL (p > 0.0001). Overall, global HRQoL worsened at 6 (p < 0.001) but returned to the baseline value at 12 months and it was statistically significantly worse in women (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: De-escalation of any TKI by 1 month ON/OFF schedule maintains the MR3.0 /MR4.0 in 81% of the patients during the first 12-24 months. No patients progressed to accelerated/blastic phase, all the patients (23.5%) losing MR3.0 regained the MR3.0 and none suffered from TKI withdrawn syndrome. The study firstly report on HRQoL in elderly CML patients moving from a continuous daily therapy to a de-escalated intermittent treatment.
Keywords: chronic myeloid leukaemia; intermittent; quality of life; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
AI—speaker honoraria from Novartis, Pfizer, and Incyte; EA—consultancy and advisory for Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, and Pfizer; GR—speaker honoraria from Novartis, Pfizer, and Incyte; MB—consultant and receiving honoraria from Novartis, Incyte, and Takeda; DR—speaker honoraria: MSD, Novartis, Gilead; advisory committees: MSD, Janssen, Gilead. All the other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Italian Multicentric Randomized OPTkIMA Trial on Fixed vs Progressive Intermittent TKI Therapy in CML Elderly Patients: 3-Years of Molecular Response and Quality of Life Monitoring After Completing the Treatment Plan.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2024 May;24(5):323-331. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2024.01.008. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2024. PMID: 38369436 Clinical Trial.
-
[Results of following up patients with chronic myeloid leukemia and a deep molecular response without tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy].Ter Arkh. 2017;89(12):86-96. doi: 10.17116/terarkh2017891286-96. Ter Arkh. 2017. PMID: 29411766 Russian.
-
Efficacy and safety of nilotinib 300 mg twice daily in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase who are intolerant to prior tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Results from the Phase IIIb ENESTswift study.Leuk Res. 2018 Apr;67:109-115. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2018.02.013. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Leuk Res. 2018. PMID: 29494928 Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic drug monitoring of imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia.Biol Pharm Bull. 2015;38(5):645-54. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b15-00103. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015. PMID: 25947908 Review.
-
Comparison of Hepatotoxicity Associated With New BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors vs Imatinib Among Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Jul 1;4(7):e2120165. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.20165. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34292334 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Imatinib treatment and longitudinal growth in pediatric patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: influence of demographic, pharmacological, and genetic factors in the German CML-PAED cohort.Haematologica. 2024 Aug 1;109(8):2555-2563. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2023.284668. Haematologica. 2024. PMID: 38497150 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
De-escalation or discontinuation of tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: A multicentral, open-label, prospective trial in China.EJHaem. 2022 Sep 19;3(4):1220-1230. doi: 10.1002/jha2.550. eCollection 2022 Nov. EJHaem. 2022. PMID: 36467815 Free PMC article.
-
Different In Vitro Models of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Show Different Characteristics: Biological Replicates Are Not Biologically Equivalent.Cell Biol Int. 2025 May;49(5):570-586. doi: 10.1002/cbin.70007. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Cell Biol Int. 2025. PMID: 40022557 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia: an overview of the new insights and biomarkers.Front Oncol. 2025 May 8;15:1546813. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1546813. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40406262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dose Optimization of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 30;17:211-225. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S532263. eCollection 2025. Clin Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40761712 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bower H, Björkholm M, Dickman PW, Höglund M, Lambert PC, Andersson TML. Life expectancy of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia approaches the life expectancy of the general population. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2851‐2857. - PubMed
-
- Rousselot P, Charbonnier A, Cony‐Makhoul P, et al. Loss of major molecular response as a trigger for restarting tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in patients with chronic‐phase chronic myelogenous leukemia who have stopped imatinib after durable undetectable disease. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(5):424‐430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

