Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms and Other Symptoms of the At-risk Mental State for Psychosis: A Network Perspective
- PMID: 33595089
- PMCID: PMC8266672
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbaa187
Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms and Other Symptoms of the At-risk Mental State for Psychosis: A Network Perspective
Abstract
Background: The high prevalence of obsessive-compulsive symptoms (OCS) among subjects at Ultra-High Risk (UHR) for psychosis is well documented. However, the network structure spanning the relations between OCS and symptoms of the at risk mental state for psychosis as assessed with the Comprehensive Assessment of At Risk Mental States (CAARMS) has not yet been investigated. This article aimed to use a network approach to investigate the associations between OCS and CAARMS symptoms in a large sample of individuals with different levels of risk for psychosis.
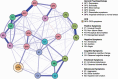
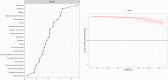
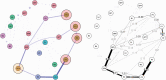
Method: Three hundred and forty-one UHR and 66 healthy participants were included, who participated in the EU-GEI study. Data analysis consisted of constructing a network of CAARMS symptoms, investigating central items in the network, and identifying the shortest pathways between OCS and positive symptoms.
Results: Strong associations between OCS and anxiety, social isolation and blunted affect were identified. Depression was the most central symptom in terms of the number of connections, and anxiety was a key item in bridging OCS to other symptoms. Shortest paths between OCS and positive symptoms revealed that unusual thought content and perceptual abnormalities were connected mainly via anxiety, while disorganized speech was connected via blunted affect and cognitive change.
Conclusions: Findings provide valuable insight into the central role of depression and the potential connective component of anxiety between OCS and other symptoms of the network. Interventions specifically aimed to reduce affective symptoms might be crucial for the development and prospective course of symptom co-occurrence.
Keywords: anxiety; clinical high risk; depression; network analysis; obsessive-compulsive; psychosis; ultra-high risk.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center.
Figures

References
-
- Swets M, Dekker J, van Emmerik-van Oortmerssen K, et al. The obsessive compulsive spectrum in schizophrenia, a meta-analysis and meta-regression exploring prevalence rates. Schizophr Res. 2014;152(2–3):458–468. - PubMed
-
- Zink M, Schirmbeck F, Rausch F, et al. Obsessive-compulsive symptoms in at-risk mental states for psychosis: associations with clinical impairment and cognitive function. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2014;130(3):214–226. - PubMed
-
- Poyurovsky M, Kriss V, Weisman G, et al. Familial aggregation of schizophrenia-spectrum disorders and obsessive-compulsive associated disorders in schizophrenia probands with and without OCD. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005;133B(1):31–36. - PubMed
-
- Soyata AZ, Akışık S, İnhanlı D, Noyan H, Üçok A. Relationship of obsessive-compulsive symptoms to clinical variables and cognitive functions in individuals at ultra high risk for psychosis. Psychiatry Res. 2018;261:332–337. - PubMed
-
- Fusar-Poli P, Cappucciati M, Bonoldi I, et al. Prognosis of brief psychotic episodes: a meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73(3):211–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

