Neuropeptidomic Profiling and Localization in the Crustacean Cardiac Ganglion Using Mass Spectrometry Imaging with Multiple Platforms
- PMID: 33595330
- PMCID: PMC7893679
- DOI: 10.1021/jasms.0c00191
Neuropeptidomic Profiling and Localization in the Crustacean Cardiac Ganglion Using Mass Spectrometry Imaging with Multiple Platforms
Abstract
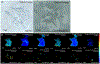
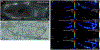
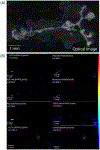
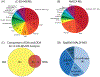
The crustacean cardiac neuromuscular system is a useful model for studying how neural circuits generate behavior, as it is comprised of a simple ganglion containing nine neurons, yet acts as a robust central pattern generator. The crustacean heart is neurogenic, receiving input from neuropeptides. However, the specific effects of neuropeptides on cardiac output is not fully understood, and the large degree of comodulation between multiple neuropeptides makes studying these effects more challenging. To address this challenge, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry (MS) imaging was used to localize neuropeptides within the cardiac ganglion (CG), providing information about the identity and localization of neuropeptides being present. CG extracts were also profiled using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) with a data independent acquisition method, resulting in the confirmation of 316 neuropeptides. Two MS imaging (MSI) platforms were compared to provide comprehensive results, including a MALDI-Orbitrap instrument for high mass spectral resolution for accurate identifications and a MALDI TOF/TOF instrument for improved spatial resolution and sensitivity, providing more descriptive MS images. MS images for 235 putative neuropeptides were obtained, with the identification of 145 of these being confirmed by either complementary MS/MS data or accurate mass matching. The MSI studies demonstrate the sensitivity and power of this MALDI-based in situ analytical strategy for unraveling the chemical complexity present in a small nine-cell neuronal system. The results of this study will enable more informative assays of the functions of neuropeptides within this important neural circuit.
Keywords: cardiac neurophysiology; crustacean; mass spectrometry imaging; neuropeptides.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mapping of neuropeptides in the crustacean stomatogastric nervous system by imaging mass spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013 Jan;24(1):134-47. doi: 10.1007/s13361-012-0502-z. Epub 2012 Nov 29. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013. PMID: 23192703 Free PMC article.
-
In situ identification and mapping of neuropeptides from the stomatogastric nervous system of Cancer borealis.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2014 Nov 30;28(22):2437-44. doi: 10.1002/rcm.7037. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2014. PMID: 25303472 Free PMC article.
-
Capillary electrophoresis coupled to MALDI mass spectrometry imaging with large volume sample stacking injection for improved coverage of C. borealis neuropeptidome.Analyst. 2019 Dec 16;145(1):61-69. doi: 10.1039/c9an01883b. Analyst. 2019. PMID: 31723949 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectral imaging and profiling of neuropeptides at the organ and cellular domains.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Aug;397(8):3185-93. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3723-7. Epub 2010 Apr 25. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20419488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropeptidomics: Improvements in Mass Spectrometry Imaging Analysis and Recent Advancements.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021;22(2):158-169. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666201116115708. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021. PMID: 33200705 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FMRFamide-like peptides (FaLPs) - an overview of diverse physiological roles in insects and other arthropods.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Mar 31;21(6):2725-2746. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.106382. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40303311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometry imaging: new eyes on natural products for drug research and development.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Dec;43(12):3096-3111. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-00990-8. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 36229602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profiling 26,000 Aplysia californica neurons by single cell mass spectrometry reveals neuronal populations with distinct neuropeptide profiles.J Biol Chem. 2022 Aug;298(8):102254. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102254. Epub 2022 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35835221 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of chemical synapses and modulatory release sites in the cardiac ganglion of the crab, Cancer borealis.J Comp Neurol. 2022 Dec;530(17):2954-2965. doi: 10.1002/cne.25385. Epub 2022 Jul 26. J Comp Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35882035 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in mass spectrometry analysis of neuropeptides.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023 Mar;42(2):706-750. doi: 10.1002/mas.21734. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023. PMID: 34558119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marder E, Bucher D: Understanding circuit dynamics using the stomatogastric nervous system of lobsters and crabs. Annu Rev Physiol. 69, 291–316 (2007) - PubMed
-
- Kuramoto T, Yamagishi H: Physiological anatomy, burst formation, and burst frequency of the cardiac ganglion of crustaceans. Physiological Zoology. 63, 102–116 (1990)
-
- Ransdell JL, Temporal S, West NL, Leyrer ML, Schulz DJ: Characterization of inward currents and channels underlying burst activity in motoneurons of crab cardiac ganglion. J Neurophysiol. 110, 42–54 (2013) - PubMed
-
- Cooke IM: Reliable, responsive pacemaking and pattern generation with minimal cell numbers: the crustacean cardiac ganglion. Biol Bull. 202, 108–136 (2002) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

