Cytoskeletal Proteins in Myotendinous Junctions of Human Extraocular Muscles
- PMID: 33595614
- PMCID: PMC7900863
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.62.2.19
Cytoskeletal Proteins in Myotendinous Junctions of Human Extraocular Muscles
Abstract
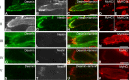
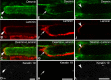
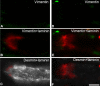
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate the cytoskeletal composition of myotendinous junctions (MTJs) in the human extraocular muscles (EOMs). Desmin and other major cytoskeletal proteins are enriched at the MTJs of ordinary myofibers, where they are proposed to be of particular importance for force transmission and required to maintain myofiber integrity.
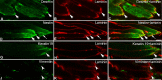
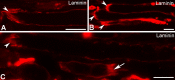
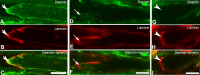
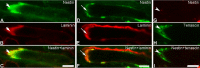
Methods: EOM and limb muscle samples were analyzed with immunohistochemistry using antibodies against the intermediate filament proteins desmin, nestin, keratin 19, vimentin, and different myosin heavy chain (MyHC) isoforms. MTJs were identified by labeling with antibodies against laminin or tenascin.
Results: In contrast to MTJs in lumbrical muscle where desmin, nestin, and keratin 19 were always present, approximately one-third of the MTJs in the EOMs lacked either desmin and/or nestin, and all MTJs lacked keratin 19. Approximately 6% of the MTJs in the EOMs lacked all of these key cytoskeletal proteins.
Conclusions: The cytoskeletal protein composition of MTJs in human EOMs differed significantly from that of MTJs in limb muscles. These differences in cytoskeletal protein composition may indicate particular adaptation to meet the functional requirements of the EOMs.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intermediate filaments in the human extraocular muscles.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Jul 15;55(8):5151-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14316. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 25028355
-
The Cytoskeleton in the Extraocular Muscles of Desmin Knockout Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Oct 1;59(12):4847-4855. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-24508. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347079
-
Intermediate filaments in the medial rectus muscles in patients with concomitant exotropia.Int Ophthalmol. 2020 Feb;40(2):403-410. doi: 10.1007/s10792-019-01197-3. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Int Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31630292
-
Cytoskeleton-associated proteins: their role as cellular integrators in the neoplastic process.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1985;3(3):191-204. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(85)80026-3. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1985. PMID: 2412718 Review.
-
Cytoskeletal disruption after eccentric contraction-induced muscle injury.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002 Oct;(403 Suppl):S90-9. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200210001-00011. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. PMID: 12394457 Review.
Cited by
-
Obscurin Maintains Myofiber Identity in Extraocular Muscles.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Feb 1;65(2):19. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.2.19. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38334702 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Selective Innervation of Extraocular Muscle Compartments.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Feb 1;64(2):24. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.2.24. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 36820678 Free PMC article.
-
Nestin and osteocrin mRNA increases in human semitendinosus myotendinous junction 7 days after a single bout of eccentric exercise.Histochem Cell Biol. 2022 Jul;158(1):49-64. doi: 10.1007/s00418-022-02101-4. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Histochem Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35428952 Clinical Trial.
-
fhl2b mediates extraocular muscle protection in zebrafish models of muscular dystrophies and its ectopic expression ameliorates affected body muscles.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 2;15(1):1950. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46187-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38431640 Free PMC article.
-
Sparing of the extraocular muscles in mdx mice with absent or reduced utrophin expression: A life span analysis.Neuromuscul Disord. 2015 Nov;25(11):873-87. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Sep 6. Neuromuscul Disord. 2015. PMID: 26429098 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

