Role of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors in vascular injury of inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 33595873
- PMCID: PMC7957208
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16333
Role of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors in vascular injury of inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
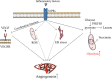
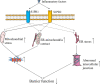
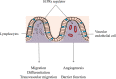
Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors (S1PRs) have an impact on the intestinal inflammation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) by regulating lymphocyte migration and differentiation. S1PR modulators as an emerging therapeutic approach are being investigated for the treatment of IBD. However, the role of S1PRs in intestinal vessels has not drawn much attention. Intestinal vascular damage is one of the major pathophysiological features of IBD, characterized by increased vascular density and impaired barrier function. S1PRs have pleiotropic effects on vascular endothelial cells, including proliferation, migration, angiogenesis and barrier homeostasis. Mounting evidence shows that S1PRs are abnormally expressed on intestinal vascular endothelial cells in IBD. Unexpectedly, S1PR modulators may damage intestinal vasculature, for example increase intestinal bleeding; therefore, S1PRs are thought to be involved in the regulation of intestinal vascular function in IBD. However, little is understood about how S1PRs regulate intestinal vascular function and participate in the initiation and progression of IBD. In this review, we summarize the pathogenic role of S1PRs in and the underlying mechanisms behind the intestinal vascular injury in IBD in order for improving IBD practice including S1PR-targeted therapies.
Keywords: inflammatory bowel disease; lymphocyte; sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor; vascular injury.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Unveiling the biological role of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulators in inflammatory bowel diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jan 7;29(1):110-125. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.110. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36683721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review article: the sphingosine 1 phosphate/sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor axis - a unique therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel disease.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Feb;55(3):277-291. doi: 10.1111/apt.16741. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34932238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of sphingosine-1-phosphate in the gut mucosal microenvironment and inflammatory bowel diseases.Front Physiol. 2023 Jul 25;14:1235656. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1235656. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37560160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipids as mediators of inflammation and novel therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel disease.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020;120:123-158. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2019.11.003. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 32085881 Review.
-
S1PR2/RhoA/ROCK1 pathway promotes inflammatory bowel disease by inducing intestinal vascular endothelial barrier damage and M1 macrophage polarization.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Jul;201:115077. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115077. Epub 2022 May 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35537530
Cited by
-
Colitis-associated carcinogenesis: crosstalk between tumors, immune cells and gut microbiota.Cell Biosci. 2023 Oct 24;13(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01139-8. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37875976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Bovine Intraepithelial T Lymphocytes in the Gut.Pathogens. 2023 Sep 19;12(9):1173. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12091173. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37764981 Free PMC article.
-
S1PR1-biased activation drives the resolution of endothelial dysfunction-associated inflammatory diseases by maintaining endothelial integrity.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 20;16(1):1826. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57124-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39979282 Free PMC article.
-
TCF12 Transcriptionally Activates SPHK1 to Induce Osteosarcoma Angiogenesis by Promoting the S1P/S1PR4/STAT3 Axis.Mol Cell Biol. 2024;44(5):178-193. doi: 10.1080/10985549.2024.2341781. Epub 2024 May 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38767243 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic sphingosine 1-phosphate pathway in psoriasis: a critical review of its pathogenic significance and potential as a therapeutic target.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Apr 18;22(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01813-3. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 37072847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wanders LK, Cordes M, Voorham Q, et al. IBD‐Associated dysplastic lesions show more chromosomal instability than sporadic adenomas. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2020;26(2):167‐180. - PubMed
-
- Lo B, Julsgaard M, Vester‐Andersen MK, Vind I, Burisch J. Disease activity, steroid use and extraintestinal manifestation are associated with increased disability in patients with inflammatory bowel disease using the inflammatory bowel disease disability index: a cross‐sectional multicentre cohort study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30:1130‐2113. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen OH, Li Y, Johansson‐Lindbom B, Coskun M. Sphingosine‐1‐phosphate signaling in inflammatory bowel disease. Trends Mol Med. 2017;23(4):362‐374. - PubMed
-
- Ma C, Battat R, Dulai PS, et al. Innovations in oral therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. Drugs. 2019;79:1321‐1335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

