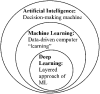
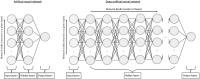
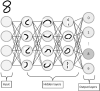
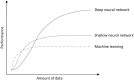
CORR Synthesis: When Should the Orthopaedic Surgeon Use Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
- PMID: 33595930
- PMCID: PMC8208440
- DOI: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001679
CORR Synthesis: When Should the Orthopaedic Surgeon Use Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
Conflict of interest statement
The authors certify that neither they, nor any members of their immediate families, have funding or commercial associations (consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article. All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research® editors and board members are on file with the publication and can be viewed on request.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Machine Learning for the Orthopaedic Surgeon: Uses and Limitations.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022 Sep 7;104(17):1586-1594. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.21.01305. Epub 2022 Apr 5. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022. PMID: 35383655
-
Artificial Intelligence Applications for Workflow, Process Optimization and Predictive Analytics.Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2020 Nov;30(4):e1-e15. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2020.08.008. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2020. PMID: 33039002 Review.
-
Basic Artificial Intelligence Techniques: Machine Learning and Deep Learning.Radiol Clin North Am. 2021 Nov;59(6):933-940. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2021.06.004. Radiol Clin North Am. 2021. PMID: 34689878 Review.
-
A practical guide to the development and deployment of deep learning models for the orthopedic surgeon: part II.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023 May;31(5):1635-1643. doi: 10.1007/s00167-023-07338-7. Epub 2023 Feb 11. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023. PMID: 36773057 Review.
-
Artificial intelligence and machine learning: an introduction for orthopaedic surgeons.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Feb;30(2):361-364. doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06741-2. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. PMID: 34528133
Cited by
-
Predicting acetabular version in native hip joints through plain x-ray radiographs: a comparative analysis of convolutional neural network model and the current gold standard, with insights and implications for hip arthroplasty.Front Surg. 2024 Oct 15;11:1329085. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1329085. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 39474228 Free PMC article.
-
Artifical intelligence use in orthopedics: an ethical point of view.EFORT Open Rev. 2023 Aug 1;8(8):592-596. doi: 10.1530/EOR-23-0083. EFORT Open Rev. 2023. PMID: 37526254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dialysis resource allocation in critical care: the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the promise of big data analytics.Front Nephrol. 2023 Oct 26;3:1266967. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2023.1266967. eCollection 2023. Front Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37965069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Regenerative Orthopedics: A Paradigm Shift in Patient Care.Cureus. 2023 Nov 30;15(11):e49756. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49756. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38161806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting the Risk of Total Hip Replacement by Using A Deep Learning Algorithm on Plain Pelvic Radiographs: Diagnostic Study.JMIR Form Res. 2023 Oct 20;7:e42788. doi: 10.2196/42788. JMIR Form Res. 2023. PMID: 37862084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akbilgic O, Davis RL. The promise of machine learning: when will it be delivered? J Card Fail . 2019;25:484-485. - PubMed
-
- Al-Helo S, Alomari RS, Ghosh S, et al. Compression fracture diagnosis in lumbar: a clinical CAD system. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg . 2013;8:461-469. - PubMed
-
- Association for Computing Machinery. Turing A.M. Award 1971. John McCarthy. Available at: https://amturing.acm.org/award_winners/mccarthy_1118322.cfm. Accessed December 13, 2020.
-
- Barnett GO, Cimino JJ, Hupp JA, Hoffer EP. An evolving diagnostic decision-support system. JAMA . 1987;258:67-74. - PubMed
-
- Basha CMAKZ, Padmaja M, Balaji GN. Computer aided fracture detection system. J Med Imaging Health Inform . 2018;8:526-531.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

