Internet of medical things (IoMT)-integrated biosensors for point-of-care testing of infectious diseases
- PMID: 33596516
- PMCID: PMC7866895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113074
Internet of medical things (IoMT)-integrated biosensors for point-of-care testing of infectious diseases
Abstract
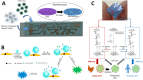
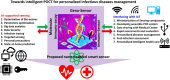
On global scale, the current situation of pandemic is symptomatic of increased incidences of contagious diseases caused by pathogens. The faster spread of these diseases, in a moderately short timeframe, is threatening the overall population wellbeing and conceivably the economy. The inadequacy of conventional diagnostic tools in terms of time consuming and complex laboratory-based diagnosis process is a major challenge to medical care. In present era, the development of point-of-care testing (POCT) is in demand for fast detection of infectious diseases along with "on-site" results that are helpful in timely and early action for better treatment. In addition, POCT devices also play a crucial role in preventing the transmission of infectious diseases by offering real-time testing and lab quality microbial diagnosis within minutes. Timely diagnosis and further treatment optimization facilitate the containment of outbreaks of infectious diseases. Presently, efforts are being made to support such POCT by the technological development in the field of internet of medical things (IoMT). The IoMT offers wireless-based operation and connectivity of POCT devices with health expert and medical centre. In this review, the recently developed POC diagnostics integrated or future possibilities of integration with IoMT are discussed with focus on emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases like malaria, dengue fever, influenza A (H1N1), human papilloma virus (HPV), Ebola virus disease (EVD), Zika virus (ZIKV), and coronavirus (COVID-19). The IoMT-assisted POCT systems are capable enough to fill the gap between bioinformatics generation, big rapid analytics, and clinical validation. An optimized IoMT-assisted POCT will be useful in understanding the diseases progression, treatment decision, and evaluation of efficacy of prescribed therapy.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Biosensor; Infectious diseases; Intelligent healthcare; Internet of medical things; Point-of-care-testing.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest declared by the authors.
Figures














References
-
- Al-Turjman F., Nawaz M.H., Ulusar U.D. Intelligence in the Internet of Medical Things era: a systematic review of current and future trends. Comput. Commun. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2019.12.030. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

