Impact of Concomitant Aberrant CD200 and BCL2 Overexpression on Outcome of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Cohort Study from a Single Center
- PMID: 33596632
- PMCID: PMC8171206
- DOI: 10.4274/tjh.galenos.2021.2020.0728
Impact of Concomitant Aberrant CD200 and BCL2 Overexpression on Outcome of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Cohort Study from a Single Center
Abstract
Objective: CD200 and BCL2 overexpression is independently associated with inferior survival in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and these two factors are frequently co-expressed; however, no data are available on the role of concomitant aberrant CD200 and BCL2 expression on outcome of AML patients. We aimed to elucidate the prognostic role of CD200/BCL2 co-expression and its association with specific leukemia subsets.
Materials and methods: We analyzed 242 adult AML patients uniformly treated with intensive chemotherapy, evaluating the impact of CD200 and BCL2 expression on complete remission (CR), disease-free survival, and overall survival (OS).
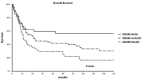
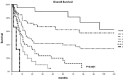
Results: CD200 and BCL2 were expressed in 139 (57.4%) and 137 (56.6%) cases, respectively, with 92 patients (38%) displaying double positivity (DP), 58 (24%) displaying double negativity (DN), and 92 patients expressing only either CD200 (n=47) or BCL2 (n=45). CR was achieved in 71% of cases, being less frequent in DP patients (60%) compared to other groups (76%-81%, p<0.001). In the whole population 3-year OS was 44%, being lower in DP patients (28%) than in patients with single CD200 or BCL2 expression (47%) or DN cases (60%; p=0.004). Other factors associated with worse OS were advanced age, CD34 positivity, secondary AML, and high white blood cell count at diagnosis; combining these 4 factors with CD200/BCL2 DP, we identified 6 groups with significantly different rates of survival (3-year OS ranging from 90% to 0%).
Conclusion: Our data support a synergistic effect of CD200 and BCL2 in AML cells, conferring an enhanced survival capacity in a permissive microenvironment and resulting in worse prognosis.
Amaç: CD200 ve BCL2 aşırı ekspresyonu, bağımsız olarak, akut myeloid lösemide (AML) düşük hayatta kalma ile ilişkilidir ve bu 2 faktör sıklıkla birlikte ifade edilir; bununla birlikte, AML hastalarının akıbeti üzerindeki eşzamanlı anormal CD200 ve BCL2 ekspresyonunun rolü hakkında hiçbir veri mevcut değildir. CD200/BCL2 birlikte ifadesinin prognostik rolünü ve bunun spesifik lösemi alt kümeleri ile ilişkisini aydınlatmayı amaçladık.
Gereç ve yöntemler: CD200 ve BCL2 ekspresyonunun tam remisyon (CR), hastalıksız sağkalım (DFS) ve genel sağkalım (OS) üzerindeki rolünü değerlendirerek, yoğun kemoterapi ile eşit şekilde tedavi edilen 242 yetişkin AML hastasını analiz ettik.
Bulgular: CD200 ve BCL2 sırasıyla 139 (%57,4) ve 137 (%56,6) olguda ifade edildi; 92 hastada (%38) çift pozitiflik (DP), 58 (%24) hastada çift negatiflik (DN) ve 92 hastada sadece CD200 (47) veya sadece BCL2 (45) ifadesi vardı . Hastaların %71’inde CR elde edildi, CR, DP hastalarında (%60) diğer gruplara göre (%76-81, p<0,001) daha düşüktü. Tüm popülasyonda 3 yıllık OS %44 olup, DP hastalarında (%28), tek CD200 veya BCL2 ekspresyonu olan hastalara (%47) göre ve DN olgularına göre (%60; p=0,004) daha düşüktür. Daha kötü OS ile ilişkili diğer faktörler ileri yaş, CD34 pozitifliği, ikincil AML ve tanıda yüksek WBC idi; Bu 4 faktörü CD200/BCL2 DP ile birleştirerek, önemli ölçüde farklı sağkalıma sahip 6 grup belirledik (3 yıllık OS %90 ila 0 arasında değişir).
Sonuç: Verilerimiz, CD200 ve BCL2’nin AML hücrelerinde sinerjistik etkisini ve kısıtlanmamış bir mikro ortamda gelişmiş bir hayatta kalma kapasitesi sağlayarak daha kötü bir prognoza neden oluşu desteklemektedir.
Keywords: BCL2; CD200; Acute myeloid leukemia; Prognosis; Survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:48–58. - PubMed
-
- Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, Johnston PG. Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:714–726. - PubMed
-
- Higgins CF. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. - PubMed
-
- Zhitomirsky B, Assaraf YG. Lysosomes as mediators of drug resistance in cancer. Drug Resist Updat. 2016;24:23–33. - PubMed
-
- Moreaux J, Veyrune JL, Reme T, De Vos J, Klein B. CD200: A putative therapeutic target in cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;366:117–122. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical