Bronchoesophageal fistula secondary to esophageal diverticulum in an adult: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 33596687
- PMCID: PMC7897816
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060521992234
Bronchoesophageal fistula secondary to esophageal diverticulum in an adult: a case report and literature review
Abstract
Esophageal diverticulum with secondary bronchoesophageal fistula is a rare clinical entity that manifests as respiratory infections, coughing during eating or drinking, hemoptysis, and sometimes fatal complications. In the present study, we describe a case of bronchoesophageal fistula emanating from esophageal diverticulum in a 45-year-old man who presented with bronchiectasis. We summarize the characteristics of this rare condition based on a review of the relevant literature.
Keywords: Esophageal diverticulum; bronchiectasis; bronchoesophageal fistula; congenital BEF; literature review; postprandial cough.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
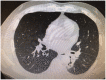
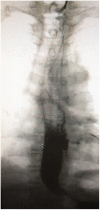
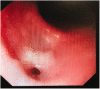
References
-
- Martins A, Gonçalves Á, Almeida T, et al. Bronchoesophageal fistula in the setting of tuberculosis infection. J Gastrointest Surg 2017; 21: 2119–2121. - PubMed
-
- Stewart WR, Klassen KP, Horava AP. Esophagobronchial fistula due to esophageal traction diverticulum; review of literature and report of case. AMA Arch Surg 1958; 76: 317–321. - PubMed
-
- Balthazar EJ. Esophagobronchial fistula secondary to ruptured traction diverticulum. Gastrointest Radiol 1977; 2: 119–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

