Personality inventory for DSM-5 brief form(PID-5-BF) in Chinese students and patients: evaluating the five-factor model and a culturally informed six-factor model
- PMID: 33596861
- PMCID: PMC7890813
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-021-03080-x
Personality inventory for DSM-5 brief form(PID-5-BF) in Chinese students and patients: evaluating the five-factor model and a culturally informed six-factor model
Abstract
Background: The Personality Inventory for DSM-5 Brief Form (PID-5-BF) is a 25-item measuring tool evaluating maladaptive personality traits for the diagnosis of personality disorders(PDs). As a promising scale, its impressive psychometric properties have been verified in some countries, however, there have been no studies about the utility of the PID-5-BF in Chinese settings. The current study aimed to explore the maladaptive personality factor model which was culturally adapted to China and to examine psychometric properties of the PID-5-BF among Chinese undergraduate students and clinical patients.
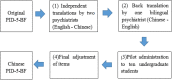
Methods: Seven thousand one hundred fifty-five undergraduate students and 451 clinical patients completed the Chinese version of the PID-5-BF. Two hundered twenty-eight students were chosen randomly for test-retest reliability at a 4-week interval. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) were conducted to discover the most suitable factor structure in China, measurement invariance(MI), internal consistency, and external validity were also calculated.
Results: The theoretical five-factor model was acceptable, but the exploratory six-factor model was more applicable in both samples (Undergraduate sample: CFI = 0.905, TLI = 0.888, RMSEA = 0.044, SRMR = 0.039; Clinical sample: CFI = 0.904, TLI = 0.886, RMSEA = 0.047, SRMR = 0.060). In the Chinese six-factor model, the Negative Affect domain was divided into two factors and the new factor was named "Interpersonal Relationships", which was in line with the Big-Six Personality model in Chinese. Measurement invariance across non-clinical and clinical sample was established (configural, weak, strong MI, and partial strict MI). Aside from acceptable internal consistency (Undergraduate sample: alpha = 0.84, MIC = 0.21; Clinical sample: alpha = 0.86, MIC = 0.19) and test-retest reliability(0.73), the correlation between the 25-item PID-5-BF and the 220-item PID-5 was significant(p < 0.01). The six PDs measured by Personality diagnostic questionnaire-4+ (PDQ-4+) were associated with and predicted by expected domains of PID-5-BF.
Conclusions: Both the theoretical five-factor model and the exploratory six-factor model of the PID-5-BF were acceptable to the Chinese population. The five-factor model could allow for comparison and integration with other work on the original theoretical model. However, the Chinese six-factor structure may be more culturally informed in East Asian settings. In sum, the PID-5-BF is a convenient and useful screening tool for personality disorders.
Keywords: Factor structure; Measurement invariance; Personality diagnostic questionnaire-4+ (PDQ-4+); Personality inventory for DSM-5-brief form (PID-5-BF); Reliability; Validity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Level of personality functioning scale-brief form 2.0: validity and reliability of the Chinese version.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):640. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-07081-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40598045 Free PMC article.
-
[Validation of a French translation of Krueger's personality inventory for DSM-5 in its brief form (PID-5 BF)].Encephale. 2018 Feb;44(1):9-13. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.07.006. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Encephale. 2018. PMID: 27692349 French.
-
Validation of the Personality Inventory for DSM-5-Brief Form (PID-5-BF) with Iranian University Students and Clinical Samples: Factor Structure, Measurement Invariance, and Convergent, Discriminant, and Known-Groups Validity.J Pers Assess. 2023 May-Jun;105(3):371-381. doi: 10.1080/00223891.2022.2152347. Epub 2022 Dec 13. J Pers Assess. 2023. PMID: 36511889
-
The Personality Inventory for DSM-5: Psychometric Evidence of Validity and Reliability-Updates.Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2020 Jul/Aug;28(4):225-237. doi: 10.1097/HRP.0000000000000261. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32692087
-
A Meta-Analysis of the Structural Validity of Original and Brief Versions of the Personality Inventory for DSM-5 in Iran.Iran J Psychiatry. 2025 Jan;20(1):126-141. doi: 10.18502/ijps.v20i1.17406. Iran J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40093526 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pre-existing Psychiatric Morbidity Is Strongly Associated to Takotsubo Syndrome: A Case-Control Study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jul 12;9:925459. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.925459. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35903670 Free PMC article.
-
Maladaptive personality traits (DSM-5 AMPD, Criterion B) and depression among medical students in Egypt: a multicentric cross-sectional study.BMC Psychol. 2025 May 7;13(1):482. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02784-z. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40336124 Free PMC article.
-
Dimensional models of personality disorders: Challenges and opportunities.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Mar 7;14:1098452. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1098452. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36960458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychometric properties of the Persian version of short-form five factor borderline inventory (FFBI-SF).BMC Psychiatry. 2022 Feb 3;22(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03667-4. BMC Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35114962 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the measurement invariance of the Personality Inventory for DSM-5 across Black and White americans.Psychol Assess. 2023 Sep;35(9):721-728. doi: 10.1037/pas0001255. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Psychol Assess. 2023. PMID: 37384515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, J. L., Sellbom, M., Bagby, R. M., Quilty, L. C., Veltri, C. O., Markon, K. E., & Krueger, R.F On the convergence between PSY-5 domains and PID-5 domains and facets: implications for assessment of DSM-5 personality traits. Assessment 2013, 20(3), 286–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 31671144/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019JJ40362/Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 13YJA190015/Chinese Ministry of Education's Humanities and Social Science Research Project
- 2017jy77/The Research Foundation of the Education Commission of Hunan Province
- 2020zzts284/the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous