Highly glycosylated MUC1 mediates high affinity L-selectin binding at the human endometrial surface
- PMID: 33596915
- PMCID: PMC7890821
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-021-00793-9
Highly glycosylated MUC1 mediates high affinity L-selectin binding at the human endometrial surface
Abstract
Background: Sialyl-Lewis X/L-selectin high affinity binding interactions between transmembrane O-glycosylated mucins proteins and the embryo have been implicated in implantation processes within the human reproductive system. However, the adhesive properties of these mucins at the endometrial cell surface are difficult to resolve due to known discrepancies between in vivo models and the human reproductive system and a lack of sensitivity in current in vitro models. To overcome these limitations, an in vitro model of the human endometrial epithelial was interrogated with single molecule force spectroscopy (SMFS) to delineate the molecular configurations of mucin proteins that mediate the high affinity L-selectin binding required for human embryo implantation.
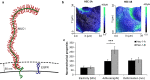
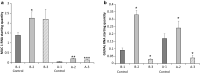
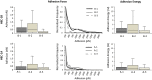
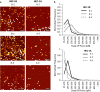
Results: This study reveals that MUC1 contributes to both the intrinsic and extrinsic adhesive properties of the HEC-1 cellular surface. High expression of MUC1 on the cell surface led to a significantly increased intrinsic adhesion force (148 pN vs. 271 pN, p < 0.001), whereas this adhesion force was significantly reduced (271 pN vs. 118 pN, p < 0.001) following siRNA mediated MUC1 ablation. Whilst high expression of MUC1 displaying elevated glycosylation led to strong extrinsic (> 400 pN) L-selectin binding at the cell surface, low expression of MUC1 with reduced glycosylation resulted in significantly less (≤200 pN) binding events.
Conclusions: An optimal level of MUC1 together with highly glycosylated decoration of the protein is critical for high affinity L-selectin binding. This study demonstrates that MUC1 contributes to cellular adhesive properties which may function to facilitate trophoblast binding to the endometrial cell surface through the L-selectin/sialyl-Lewis x adhesion system subsequent to implantation.
Keywords: Adhesion; Biophysics; Human reproduction; Implantation; Mucin; Single molecule force spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of sialyl-Lewis a-carrying CD43 and MUC1 mucins secreted from a colon carcinoma cell line for E-selectin binding and inhibition of leukocyte adhesion.Tumour Biol. 1997;18(3):175-87. doi: 10.1159/000218028. Tumour Biol. 1997. PMID: 9143414
-
Tumor cell MUC1 and CD43 are glycosylated differently with sialyl-Lewis a and x epitopes and show variable interactions with E-selectin under physiological flow conditions.Glycoconj J. 2001 Nov-Dec;18(11-12):925-30. doi: 10.1023/a:1022208727512. Glycoconj J. 2001. PMID: 12820726
-
Secreted MUC1 mucins lacking their cytoplasmic part and carrying sialyl-Lewis a and x epitopes from a tumor cell line and sera of colon carcinoma patients can inhibit HL-60 leukocyte adhesion to E-selectin-expressing endothelial cells.J Cell Biochem. 1996 Mar 15;60(4):538-49. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19960315)60:4%3C538::AID-JCB10%3E3.0.CO;2-D. J Cell Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8707893
-
Diverse glycosylation of MUC1 and MUC2: potential significance in tumor immunity.J Biochem. 1999 Dec;126(6):975-85. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022565. J Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10578046 Review.
-
MUC1 and endometrial receptivity.Mol Hum Reprod. 1998 Dec;4(12):1089-98. doi: 10.1093/molehr/4.12.1089. Mol Hum Reprod. 1998. PMID: 9872358 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Insights into Human Endometrial Peptidases in Blastocyst Implantation via Shedding of Microvesicles.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 15;22(24):13479. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413479. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lewis x-carrying O-glycans are candidate modulators for conceptus attachment in pigs†.Biol Reprod. 2023 Feb 13;108(2):292-303. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioac204. Biol Reprod. 2023. PMID: 36401880 Free PMC article.
-
When the Embryo Meets the Endometrium: Identifying the Features Required for Successful Embryo Implantation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 29;25(5):2834. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052834. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endometrial immune profiling and precision therapy increase live birth rate after embryo transfer: a randomised controlled trial.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 24;16:1523871. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1523871. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40066441 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Unique Tropism and Entry Mechanism of Mumps Virus.Viruses. 2021 Sep 1;13(9):1746. doi: 10.3390/v13091746. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34578327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/G01776X/1/BBSRC
- MC_PC_19053/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 80885/Ireland Wales 2014-2020 European Territorial Co-operation programme CALIN
- 2017/COL/004/West Wales and the Valleys European Regional Development Fund Operational Programme
- 2017/COL/001/West Wales and the Valleys European Regional Development Fund Operational Programme
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

