Chronic intermittent hypoxia promoted lung cancer stem cell-like properties via enhancing Bach1 expression
- PMID: 33596919
- PMCID: PMC7890965
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-021-01655-6
Chronic intermittent hypoxia promoted lung cancer stem cell-like properties via enhancing Bach1 expression
Abstract
Background: An adverse role for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in cancer aggressiveness and mortality has recently emerged from clinical and animal studies, and the reasons have not been fully determined. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are regarded as the main cause of carcinoma metastasis. So far, the relationship between OSA and lung CSCs has not been explored.
Method: In the present study, we established an orthotopic mouse model of primary lung cancer and utilized chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) exposure to mimic OSA status.
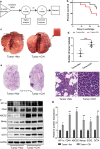
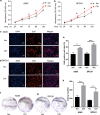
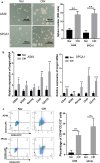
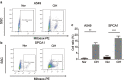
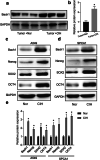
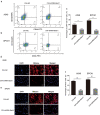
Results: We observed that CIH endows lung cancer with greater metastatic potential, evidenced by increased tumor growth, tumor seeding, and upregulated CSC-related gene expression in the lungs. Notably, the transcription factor BTB and CNC homology 1 (Bach1), a key factor in responding to conditions of oxidative stress, is increased in lung cancer after CIH exposure in vitro and in vivo. Meanwhile, exposing lung cancer cells to CIH promoted cell proliferation, clonal diversity, induced stem-like cell marker expression, and gave rise to CSCs at a relatively higher frequency. Furthermore, the increase of mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) and CSC-marker expression induced by CIH exposure was abolished in Bach1 shRNA-treated lung cancer cells.
Conclusions: Our results indicated that CIH promoted lung CSC-like properties by activating mtROS, which was partially mediated by Bach1.
Keywords: Bach1; Cancer stem cells; Chronic intermittent hypoxia; Lung cancer; Obstructive sleep apnea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BTB and CNC homology 1 (Bach1) induces lung cancer stem cell phenotypes by stimulating CD44 expression.Respir Res. 2021 Dec 23;22(1):320. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01918-2. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 34949193 Free PMC article.
-
ESM1/HIF‑1α pathway modulates chronic intermittent hypoxia‑induced non‑small‑cell lung cancer proliferation, stemness and epithelial‑mesenchymal transition.Oncol Rep. 2021 Mar;45(3):1226-1234. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7913. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33650648
-
Effect of chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced HIF-1α/ATAD2 expression on lung cancer stemness.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Jun 7;27(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00345-5. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35672694 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Therapeutic Target, BACH1, Regulates Cancer Metabolism.Cells. 2021 Mar 12;10(3):634. doi: 10.3390/cells10030634. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33809182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BACH1, the master regulator gene: A novel candidate target for cancer therapy.Gene. 2016 Aug 15;588(1):30-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.04.040. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Gene. 2016. PMID: 27108804 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic and Cycling Hypoxia: Drivers of Cancer Chronic Inflammation through HIF-1 and NF-κB Activation: A Review of the Molecular Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10701. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910701. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of cancer stem cell: regulatory factors elucidation and cancer treatment strategies.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 2;43(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03021-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38561775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia promotes conversion to a stem cell phenotype in prostate cancer cells by activating HIF-1α/Notch1 signaling pathway.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Jul;25(7):2138-2152. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03093-w. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36757381
-
Canonical and noncanonical NOTCH signaling in the nongenetic resistance of cancer: distinct and concerted control.Front Med. 2025 Feb;19(1):23-52. doi: 10.1007/s11684-024-1107-1. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Front Med. 2025. PMID: 39745621 Review.
-
Age Differences in the Association of Sleep Duration Trajectory With Cancer Risk and Cancer-Specific Mortality: Prospective Cohort Study.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Feb 7;10:e50836. doi: 10.2196/50836. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 38324354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Santamaria-Martos F, Benítez I, Girón C, Barbé F, Martínez-García MA, Hernández L, Montserrat JM, Nagore E, Martorell A, Campos-Rodriguez F, et al. Biomarkers of carcinogenesis and tumour growth in patients with cutaneous melanoma and obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J. 2018 doi: 10.1183/13993003.01885-2017. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

