Circ_0082182 promotes oncogenesis and metastasis of colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo by sponging miR-411 and miR-1205 to activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 33596920
- PMCID: PMC7891146
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-021-02164-y
Circ_0082182 promotes oncogenesis and metastasis of colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo by sponging miR-411 and miR-1205 to activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a class of endogenous single-strand RNA transcripts with crucial regulation in human cancers. The objective of this study is to investigate the role of circ_0082182 in CRC and its specific functional mechanism.
Methods: The quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed to measure the levels of circ_0082182, microRNA-411 (miR-411) and microRNA-1205 (miR-1205). Cell proliferation was detected by Cell counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and colony formation assays. Flow cytometry was used for determining cell cycle and cell apoptosis. Cell apoptosis was also assessed by caspase3 and caspase9 activities. Cell migration and invasion were examined using scratch assay and transwell assay. The interaction between circ_0082182 and miRNA was validated by the dual-luciferase reporter and biotinylated RNA pull-down assays. Wnt/β-catenin pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-associated proteins were quantified by Western blot. Xenograft model was established for the research of circ_0082182 in vivo.
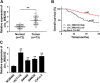
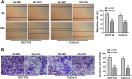
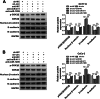
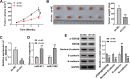
Results: Circ_0082182 was upregulated in CRC and could predict the poor prognosis of CRC patients. Functionally, circ_0082182 promoted CRC cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and metastasis while inhibited apoptosis. Subsequently, circ_0082182 was shown to act as the sponges of miR-411 and miR-1205. MiR-411 and miR-1205 were identified as tumor inhibitors in CRC. Furthermore, circ_0082182 promoted the CRC progression via sponging miR-411 and miR-1205. Moreover, circ_0082182 facilitated the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and EMT process by targeting miR-411 and miR-1205. In vivo, circ_0082182 accelerated the CRC tumorigenesis and EMT process by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by downregulating the expression of miR-411 or miR-1205.
Conclusion: This study showed that circ_0082182 functioned as an oncogene in the developing process of CRC by sponging miR-411 or miR-1205 to activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Circ_0082182 might be a molecular target in the diagnosis and treatment of CRC.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Wnt/β-catenin pathway; circ_0082182; miR-1205; miR-411.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

