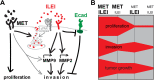
The FAM3C locus that encodes interleukin-like EMT inducer (ILEI) is frequently co-amplified in MET-amplified cancers and contributes to invasiveness
- PMID: 33596971
- PMCID: PMC7890988
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-01862-5
The FAM3C locus that encodes interleukin-like EMT inducer (ILEI) is frequently co-amplified in MET-amplified cancers and contributes to invasiveness
Abstract
Background: Gene amplification of MET, which encodes for the receptor tyrosine kinase c-MET, occurs in a variety of human cancers. High c-MET levels often correlate with poor cancer prognosis. Interleukin-like EMT inducer (ILEI) is also overexpressed in many cancers and is associated with metastasis and poor survival. The gene for ILEI, FAM3C, is located close to MET on chromosome 7q31 in an amplification "hotspot", but it is unclear whether FAMC3 amplification contributes to elevated ILEI expression in cancer. In this study we have investigated FAMC3 copy number gain in different cancers and its potential connection to MET amplifications.
Methods: FAMC3 and MET copy numbers were investigated in various cancer samples and 200 cancer cell lines. Copy numbers of the two genes were correlated with mRNA levels, with relapse-free survival in lung cancer patient samples as well as with clinicopathological parameters in primary samples from 49 advanced stage colorectal cancer patients. ILEI knock-down and c-MET inhibition effects on proliferation and invasiveness of five cancer cell lines and growth of xenograft tumors in mice were then investigated.
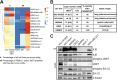
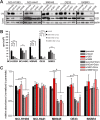
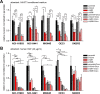
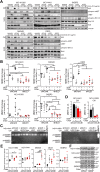
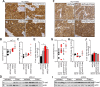
Results: FAMC3 was amplified in strict association with MET amplification in several human cancers and cancer cell lines. Increased FAM3C and MET copy numbers were tightly linked and correlated with increased gene expression and poor survival in human lung cancer and with extramural invasion in colorectal carcinoma. Stable ILEI shRNA knock-down did not influence proliferation or sensitivity towards c-MET-inhibitor induced proliferation arrest in cancer cells, but impaired both c-MET-independent and -dependent cancer cell invasion. c-MET inhibition reduced ILEI secretion, and shRNA mediated ILEI knock-down prevented c-MET-signaling induced elevated expression and secretion of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9. Combination of ILEI knock-down and c-MET-inhibition significantly reduced the invasive outgrowth of NCI-H441 and NCI-H1993 lung tumor xenografts by inhibiting proliferation, MMP expression and E-cadherin membrane localization.
Conclusions: These novel findings suggest MET amplifications are often in reality MET-FAM3C co-amplifications with tight functional cooperation. Therefore, the clinical relevance of this frequent cancer amplification hotspot, so far dedicated purely to c-MET function, should be re-evaluated to include ILEI as a target in the therapy of c-MET-amplified human carcinomas.
Keywords: C-MET; Cancer; FAM3C; Gene amplification; Interleukin-like EMT inducer (ILEI); Invasion; Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hyman E, Kauraniemi P, Hautaniemi S, Wolf M, Mousses S, Rozenblum E, et al. Impact of DNA amplification on gene expression patterns in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62(21):6240–6245. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

