Long non-coding RNA MAPKAPK5-AS1/PLAGL2/HIF-1α signaling loop promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression
- PMID: 33596983
- PMCID: PMC7891009
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-01868-z
Long non-coding RNA MAPKAPK5-AS1/PLAGL2/HIF-1α signaling loop promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression
Abstract
Background: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are widely involved in human cancers' progression by regulating tumor cells' various malignant behaviors. MAPKAPK5-AS1 has been recognized as an oncogene in colorectal cancer. However, the biological role of MAPKAPK5-AS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has not been explored.
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR was performed to detect the level of MAPKAPK5-AS1 in HCC tissues and cell lines. The effects of MAPKAPK5-AS1 on tumor growth and metastasis were assessed via in vitro experiments, including MTT, colony formation, EdU, flow cytometry, transwell assays, and nude mice models. The western blotting analysis was carried out to determine epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers and AKT signaling. The interaction between MAPKAPK5-AS1, miR-154-5p, and PLAGL2 were explored by luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation. The regulatory effect of HIF-1α on MAPKAPK5-AS1 was evaluated by chromatin immunoprecipitation.
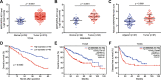
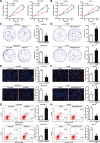
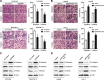
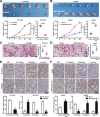
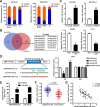
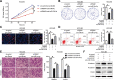
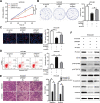
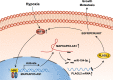
Results: MAPKAPK5-AS1 expression was significantly elevated in HCC, and its overexpression associated with malignant clinical features and reduced survival. Functionally, MAPKAPK5-AS1 knockdown repressed the proliferation, mobility, and EMT of HCC cells and induced apoptosis. Ectopic expression of MAPKAPK5-AS1 contributed to HCC cell proliferation and invasion in vitro. Furthermore, MAPKAPK5-AS1 silencing suppressed, while MAPKAPK5-AS1 overexpression enhanced HCC growth and lung metastasis in vivo. Mechanistically, MAPKAPK5-AS1 upregulated PLAG1 like zinc finger 2 (PLAGL2) expression by acting as an endogenous competing RNA (ceRNA) to sponge miR-154-5p, thereby activating EGFR/AKT signaling. Importantly, rescue experiments demonstrated that the miR-154-5p/PLAGL2 axis mediated the function of MAPKAPK5-AS1 in HCC cells. Interestingly, we found that hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), a transcript factor, could directly bind to the promoter to activate MAPKAPK5-AS1 transcription. MAPKAPK5-AS1 regulated HIF-1α expression through PLAGL2 to form a hypoxia-mediated MAPKAPK5-AS1/PLAGL2/HIF-1α signaling loop in HCC.
Conclusions: Our results reveal a MAPKAPK5-AS1/PLAGL2/HIF-1α signaling loop in HCC progression and suggest that MAPKAPK5-AS1 could be a potential novel therapeutic target of HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma progression; Hypoxia; MAPKAPK5-AS1; PLAGL2; miR-154-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MAPKAPK5-AS1 drives the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating miR-429/ZEB1 axis.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Apr 25;23(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12860-022-00420-x. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35468721 Free PMC article.
-
A novel lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting miR-194-5p/FOXA1 axis.Mol Cancer. 2019 Feb 19;18(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-0957-7. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30782188 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA AGAP2-AS1, functioning as a competitive endogenous RNA, upregulates ANXA11 expression by sponging miR-16-5p and promotes proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 14;38(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1188-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. Retraction in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Nov 2;41(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02521-z. PMID: 31088485 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Upregulation of lncRNA NIFK-AS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma by m6A methylation promotes disease progression and sorafenib resistance.Hum Cell. 2021 Nov;34(6):1800-1811. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00587-z. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 34374933 Review.
-
Effects of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and hypoxia-inducible factor-2α overexpression on hepatocellular carcinoma survival: A systematic review with meta-analysis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Jun;36(6):1487-1496. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15395. Epub 2021 Jan 26. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33393670
Cited by
-
Construction of a prognostic prediction model in liver cancer based on genes involved in integrin cell surface interactions pathway by multi-omics screening.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 5;12:1237445. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1237445. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38374893 Free PMC article.
-
MAPKAPK5-AS1 drives the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating miR-429/ZEB1 axis.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Apr 25;23(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12860-022-00420-x. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35468721 Free PMC article.
-
PLAG1 interacts with GPX4 to conquer vulnerability to sorafenib induced ferroptosis through a PVT1/miR-195-5p axis-dependent manner in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 May 14;43(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03061-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38745179 Free PMC article.
-
The hsa_circ_0000276-ceRNA regulatory network and immune infiltration in cervical cancer.BMC Cancer. 2023 Mar 9;23(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10636-5. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36894874 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the nexus between long non-coding RNAs and endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma: biomarker discovery and therapeutic horizons.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Oct 24;10(1):451. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02200-2. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39448589 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

