Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 Supports the Establishment of Chronic Gammaherpesvirus Infection in a Route- and Dose-Dependent Manner
- PMID: 33597211
- PMCID: PMC8104109
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02208-20
Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 Supports the Establishment of Chronic Gammaherpesvirus Infection in a Route- and Dose-Dependent Manner
Abstract
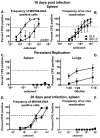
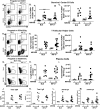
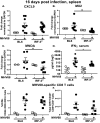
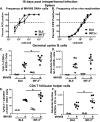
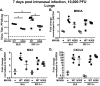
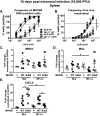
Gammaherpesviruses are ubiquitous pathogens that establish lifelong infections and are associated with several malignancies, including B cell lymphomas. Uniquely, these viruses manipulate B cell differentiation to establish long-term latency in memory B cells. This study focuses on the interaction between gammaherpesviruses and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF-3), a ubiquitously expressed transcription factor with multiple direct target genes, including beta interferon (IFN-β), a type I IFN. IRF-3 attenuates acute replication of a plethora of viruses, including gammaherpesvirus. Furthermore, IRF-3-driven IFN-β expression is antagonized by the conserved gammaherpesvirus protein kinase during lytic virus replication in vitro In this study, we have uncovered an unexpected proviral role of IRF-3 during chronic gammaherpesvirus infection. In contrast to the antiviral activity of IRF-3 during acute infection, IRF-3 facilitated establishment of latent gammaherpesvirus infection in B cells, particularly, germinal center and activated B cells, the cell types critical for both natural infection and viral lymphomagenesis. This proviral role of IRF-3 was further modified by the route of infection and viral dose. Furthermore, using a combination of viral and host genetics, we show that IRF-3 deficiency does not rescue attenuated chronic infection of a protein kinase null gammaherpesvirus mutant, highlighting the multifunctional nature of the conserved gammaherpesvirus protein kinases in vivo In summary, this study unveils an unexpected proviral nature of the classical innate immune factor, IRF-3, during chronic virus infection.IMPORTANCE Interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF-3) is a critical component of the innate immune response, in part due to its transactivation of beta interferon (IFN-β) expression. Similar to that observed in all acute virus infections examined to date, IRF-3 suppresses lytic viral replication during acute gammaherpesvirus infection. Because gammaherpesviruses establish lifelong infection, this study aimed to define the antiviral activity of IRF-3 during chronic infection. Surprisingly, we found that, in contrast to acute infection, IRF-3 supported the establishment of gammaherpesvirus latency in splenic B cells, revealing an unexpected proviral nature of this classical innate immune host factor.
Keywords: B cell responses; IRF-3; chronic infection; gammaherpesvirus; interferon.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


References
-
- Au WC, Moore PA, Lowther W, Juang YT, Pitha PM. 1995. Identification of a member of the interferon regulatory factor family that binds to the interferon-stimulated response element and activates expression of interferon-induced genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:11657–11661. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.25.11657. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sato M, Suemori H, Hata N, Asagiri M, Ogasawara K, Nakao K, Nakaya T, Katsuki M, Noguchi S, Tanaka N, Taniguchi T. 2000. Distinct and essential roles of transcription factors IRF-3 and IRF-7 in response to viruses for IFN-alpha/beta gene induction. Immunity 13:539–548. doi:10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00053-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

