Recommendations from the European Commission Initiative on Breast Cancer for multigene testing to guide the use of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early breast cancer, hormone receptor positive, HER-2 negative
- PMID: 33597715
- PMCID: PMC8076250
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-020-01247-z
Recommendations from the European Commission Initiative on Breast Cancer for multigene testing to guide the use of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early breast cancer, hormone receptor positive, HER-2 negative
Abstract
Background: Predicting the risk of recurrence and response to chemotherapy in women with early breast cancer is crucial to optimise adjuvant treatment. Despite the common practice of using multigene tests to predict recurrence, existing recommendations are inconsistent. Our aim was to formulate healthcare recommendations for the question "Should multigene tests be used in women who have early invasive breast cancer, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, to guide the use of adjuvant chemotherapy?"
Methods: The European Commission Initiative on Breast Cancer (ECIBC) Guidelines Development Group (GDG), a multidisciplinary guideline panel including experts and three patients, developed recommendations informed by systematic reviews of the evidence. Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) Evidence to Decision frameworks were used. Four multigene tests were evaluated: the 21-gene recurrence score (21-RS), the 70-gene signature (70-GS), the PAM50 risk of recurrence score (PAM50-RORS), and the 12-gene molecular score (12-MS).
Results: Five studies (2 marker-based design RCTs, two treatment interaction design RCTs and 1 pooled individual data analysis from observational studies) were included; no eligible studies on PAM50-RORS or 12-MS were identified and the GDG did not formulate recommendations for these tests.
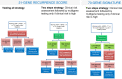
Conclusions: The ECIBC GDG suggests the use of the 21-RS for lymph node-negative women (conditional recommendation, very low certainty of evidence), recognising that benefits are probably larger in women at high risk of recurrence based on clinical characteristics. The ECIBC GDG suggests the use of the 70-GS for women at high clinical risk (conditional recommendation, low certainty of evidence), and recommends not using 70-GS in women at low clinical risk (strong recommendation, low certainty of evidence).
Conflict of interest statement
Members of the Guideline Development Group (GDG) do not receive financial compensation for their work but are reimbursed by the E.C. for travel-related expenses for the meetings organised by the JRC. Dr. Giorgi Rossi as former-PI of an independent study on HPV-based cervical cancer screening, funded by the Italian Ministry of Health, data owner, conducted negotiations with Roche diagnostics, Hologic-Genprobe, Becton-Dickinson to obtain reagents at reduced price or for free; the reagents obtained were not used in his institution. Dr. Lebeau reports grants and reimbursement for travel-related expenses related to consultancy from Roche Pharma AG, reimbursement for travel-related expenses related to consultancy from Novartis Oncology, and grants from BioNTech Diagnostics GmbH outside the submitted work. Dr. Saz-Parkinson was employed by the European Commission, coordinating the ECIBC Guidelines Development Group. Dr. Quinn is Chair of the European Working Group for Breast Screening Pathology (EWGBSP). Various companies have provided some sponsorship to the EWGBSP for group meetings. Dr. Gräwingholt is the responsible radiologist for screening unit Paderborn, Germany, consultant radiologist for screening programs in Switzerland, and consultant radiologist for Hellenic School of Senology. Dr. Canelo-Aybar, Dr. Rigau, Dr. Posso Rivera, and Dr. Alonso-Coello reports that his institution received payments from the European Commission to develop the systematic reviews informing the recommendations. Authors not named here have disclosed no conflicts of interest. Disclosures can also be viewed at
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay JEM, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, et al. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2018.
-
- ECIS. European Cancer Information System From https://ecis.jrc.ec.europa.eu (2019).
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;365:1687–1717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

