Survival from breast cancer in women with a BRCA2 mutation by treatment
- PMID: 33597716
- PMCID: PMC8076275
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-020-01164-1
Survival from breast cancer in women with a BRCA2 mutation by treatment
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Survival from breast cancer in women with a BRCA2 mutation by treatment.Br J Cancer. 2023 Feb;128(4):703. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-02130-9. Br J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36639528 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The impact of various breast-cancer treatments on patients with a BRCA2 mutation has not been studied. We sought to estimate the impact of bilateral oophorectomy and other treatments on breast cancer-specific survival among patients with a germline BRCA2 mutation.
Methods: We identified 664 women with stage I-III breast cancer and a BRCA2 mutation by combining five different datasets (retrospective and prospective). Subjects were followed for 7.2 years from diagnosis to death from breast cancer. Tumour characteristics and cancer treatments were patient-reported and derived from medical records. Predictors of survival were determined using Cox proportional hazard models, adjusted for other treatments and for prognostic features.
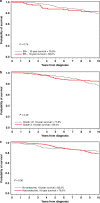
Results: The 10-year breast-cancer survival for ER-positive patients was 78.9% and for ER-negative patients was 82.3% (adjusted HR = 1.23 (95% CI, 0.62-2.45, p = 0.55)). The 10-year breast-cancer survival for women who had a bilateral oophorectomy was 89.1% and for women who did not have an oophorectomy was 59.0% (adjusted HR = 0.45; 95% CI, 0.28-0.72, p = 0.001). The adjusted hazard ratio for chemotherapy was 0.83 (95% CI, 0.65-1.53: p = 0.56).
Conclusions: For women with breast cancer and a germline BRCA2 mutation, positive ER status does not predict superior survival. Oophorectomy is associated with a reduced risk of death from breast cancer and should be considered in the treatment plan.
Conflict of interest statement
Steven A. Narod is a board member of BJC. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

