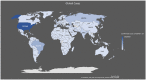
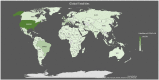
Global Pandemicity of COVID-19: Situation Report as of June 9, 2020
- PMID: 33597811
- PMCID: PMC7863149
- DOI: 10.1177/1178633721991260
Global Pandemicity of COVID-19: Situation Report as of June 9, 2020
Abstract
A novel coronavirus was identified as the cause of a cluster of pneumonia cases in Wuhan, China in December 2019. This cluster quickly spread across the globe and led the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) a pandemic on March 11, 2020. It's sudden emergence, ceaseless human-to-human transmission, and rapid spread has led to continuous pandemicity. As of June 9, 2020, there were 7 039 918 confirmed cases and 404 396 deaths globally. The rate of spread of COVID-19 is affected through respiratory droplets, most commonly when infected individuals cough or talk. The virus is released through respiratory secretions that infect individuals once contact with mucous membranes is made directly or indirectly. Our research was conducted via an electronic literature review on PubMed, Google Scholar, and MedLine Plus. Data were then collected from peer-reviewed articles that included applicable keywords and published between January 1, 2020, and June 9, 2020. This article highlights the rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 worldwide and indicates a higher number of mortalities in the elderly and those with comorbidities. As the number of cases increases, an immediate need to "flatten the curve" is essential to avoid catastrophic overwhelming of hospital systems across the affected countries. To do so, there is an emphasis on detection, testing, isolating the infected, and organizing the healthcare response to the virus. The rapid spread of infection has impacted over 200 countries and territories to date. This report takes a closer look at the cases, fatalities, and recoveries in different regions of the world with details regarding the geographic scale of SARS-CoV-2 spread, risks, and the subsequent impact on the countries affected. Also, this report discusses some effective measures that were carried out by some countries that helped them to mitigate the pandemic and flatten the curve of COVID-19 spread as early as possible.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2; global outbreak; pandemic.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests:The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- CDC. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation reports. Centers for Disease Control; 2020. Accessed April 30, 2020 https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/summary.html#cov...
-
- Ralph R, Lew J, Zeng T, et al. 2019-nCoV (Wuhan virus), a novel coronavirus: human-to-human transmission, travel-related cases, and vaccine readiness. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2020;14:3-17. - PubMed
-
- Special Expert Group for Control of the Epidemic of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia of the Chinese Preventative Medicine Association. An update on the epidemiological characteristics of novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19). Chin J Epidemiol. 2020;41:139-144.
-
- WHO. Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) situation reports—30. World Health Organization; 2020. Accessed March 24, 2020 https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous