Identification of MicroRNA-Potassium Channel Messenger RNA Interactions in the Brain of Rats With Post-traumatic Epilepsy
- PMID: 33597846
- PMCID: PMC7882489
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.610090
Identification of MicroRNA-Potassium Channel Messenger RNA Interactions in the Brain of Rats With Post-traumatic Epilepsy
Abstract
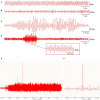
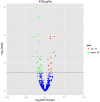
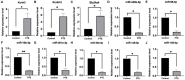
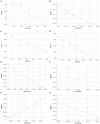
Background: Dysregulated expression of microRNAs and potassium channels have been reported for their contributions to seizure onset. However, the microRNA-potassium channel gene interactions in traumatic brain injury-induced post-traumatic epilepsy (PTE) remain unknown. Methods: PTE was induced in male rats by intracranial injection with ferrous chloride (0.1 mol/L, 1 μl/min) at the right frontal cortex. Electroencephalography was recorded at 60 min, as well as day 1, 7, and 30, and the behavioral seizures were assessed before injection and at different time points after injection. Rats were killed on day 30 after injection. The right frontal cortex samples were collected and subjected to high throughput messenger RNA (mRNA) and microRNA sequencing. A network of differentially expressed potassium channel mRNAs and microRNAs was constructed using OryCun2.0 and subjected to Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analyses. The differential mRNA and microRNA expressions were verified using quantitative real-time-PCR. The microRNA-mRNA was subject to the Pearson correlation analysis. Results: A PTE rat model was successfully established, as evidenced by behavioral seizures and epileptiform discharges on electroencephalography in PTE rats compared with sham rats. Among the 91 mRNAs and 40 microRNAs that were significantly differentially expressed in the PTE rat brain, 4 mRNAs and 10 microRNAs were associated with potassium channels. Except for potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily N member 2, the other three potassium channel mRNAs were negatively correlated with seven microRNAs. These microRNA-mRNA pairs were enriched in annotations and pathways related to neuronal ion channels and neuroinflammation. Quantitative real-time-PCR and correlation analysis verified negative correlations in miR-449a-5p-KCNH2, miR-98-5p-KCNH2, miR-98-5p-KCNK15, miR-19b-3p-KCNK15, and miR-301a-3p-KCNK15 pairs. Conclusion: We identified microRNA-potassium channel mRNA interactions associated with PTE, providing potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for PTE.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; gene annotation; microRNA; post-traumatic epilepsy; potassium channel.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Ma, Zhou, Jia, Zhan, Tan, Wang, Yang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of miRNA-mRNA regulatory network associated with the glutamatergic system in post-traumatic epilepsy rats.Front Neurol. 2022 Dec 23;13:1102672. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1102672. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36619916 Free PMC article.
-
A preliminary study of calcium channel-associated mRNA and miRNA networks in post-traumatic epileptic rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 11;13(1):13103. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39485-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37567882 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Validation of Circulating microRNAs as Biomarkers for Epileptogenesis after Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury-The EPITARGET Cohort.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 1;24(3):2823. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032823. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769143 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in cardiac pathology in Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1 transgenic mice.Physiol Genomics. 2018 Oct 1;50(10):846-861. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00048.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Physiol Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30029588 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA inhibition upregulates hippocampal A-type potassium current and reduces seizure frequency in a mouse model of epilepsy.Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Oct;130:104508. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104508. Epub 2019 Jun 15. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 31212067 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of exosomal microRNAs in central nervous system diseases.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 May;476(5):2111-2124. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04053-0. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33528706 Review.
-
miR-98-5p Prevents Hippocampal Neurons from Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis by Targeting STAT3 in Epilepsy in vitro.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023 Oct 30;19:2319-2329. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S415597. eCollection 2023. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023. PMID: 37928166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bekenstein U., Mishra N., Milikovsky D. Z., Hanin G., Zelig D., Sheintuch L., et al. . (2017). Dynamic changes in murine forebrain miR-211 expression associate with cholinergic imbalances and epileptiform activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, E4996–E5005. 10.1073/pnas.1701201114 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

