The First Word Recalled Measure - A Potential Addition to Clinical Exams
- PMID: 33597914
- PMCID: PMC7882623
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.561824
The First Word Recalled Measure - A Potential Addition to Clinical Exams
Abstract
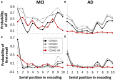
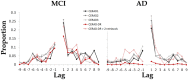
Characterizing episodic memory abilities is highly important in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and usually includes wordlist learning and recall tasks. Clinical evaluations typically focus on the number of words recalled, ignoring additional information, like serial position. Here, we tested the potential value of two serial positioning measures for clinical diagnosis - how retrieval is initiated, as measured by the first word recalled, and how it proceeds - using data from patients with AD and MCI that completed a wordlist learning and recall task. Our results show that during the early stages of learning, patients with AD are less prone to retrieve the first word from the wordlist, manifested as lower primacy effect in the first word recalled, compared with MCI patients. The first word recalled measure adds to the differentiation between the groups over and above the total number of words learned. Thus, the first word recalled during word list learning and recall tasks may be used as a simple complementary measure to distinguish between MCI and AD during standard neuropsychological evaluations.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; differential diagnosis; memory; mild cognitive impairment; neuropsychological tests.
Copyright © 2021 Shapira-Lichter, Oren, Asvadurian, Ben-Hayun, Fisher, Aharon-Peretz and Glik.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serial position effects on list learning tasks in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.Neuropsychology. 2020 May;34(4):467-478. doi: 10.1037/neu0000620. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Neuropsychology. 2020. PMID: 31999168 Review.
-
Serial position effects in patients with mild cognitive impairment and early and moderate Alzheimer's disease compared with healthy comparison subjects.Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2014;37(1-2):19-26. doi: 10.1159/000351675. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2014. PMID: 24107650
-
How many items from a word list can Alzheimer's disease patients and normal controls recall? Do they recall in a similar way?Dement Neuropsychol. 2007 Jan-Mar;1(1):52-58. doi: 10.1590/S1980-57642008DN10100009. Dement Neuropsychol. 2007. PMID: 29213368 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of the serial position effect as an early marker of Alzheimer's disease in Spanish-English bilinguals.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2024 Feb;30(2):162-171. doi: 10.1017/S1355617723000310. Epub 2023 Jun 21. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2024. PMID: 37340671
-
[Neuropsychological impairment in the early Alzheimer's disease].Encephale. 2007 May-Jun;33(3 Pt 1):310-6. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(07)92044-8. Encephale. 2007. PMID: 17675928 Review. French.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

