Probiotic potential and anticancer properties of Pediococcus sp. isolated from traditional dairy products
- PMID: 33598413
- PMCID: PMC7868823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.btre.2021.e00593
Probiotic potential and anticancer properties of Pediococcus sp. isolated from traditional dairy products
Abstract
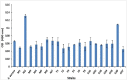
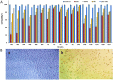
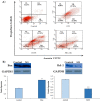
Herein, 18 lactic acid bacteria isolated from 30 samples of traditional dairy products were identified, and their probiotic potential was evaluated. According to the results, almost all strains showed the probiotic properties sufficiently, though M1 had better characterise. 16S rRNA gene sequencing revealed that this strain belongs to the Pediococcus sp. (<95 % similarity). This strain had substantial antipathogenic activity and did not show any worrying antibiotic resistance. Also, the strain was resistant to high concentrations of bile salt (1 %), NaCl (6.5 %), and low pH (2). Furthermore, it was revealed that cell-free supernatant (CFS), heat-killed cells and live cells derived from M1 significantly decreased the viability of MCF-7 cells so that the CFS resulted in 85 % cell death. Flow cytometry and western blot analysis determined that this compound induced apoptosis in the cancerous cells through increasing the BAX protein expression and decreasing the Bcl-2 protein expression.
Keywords: Anti-cancer; Apoptosis; Bacterial derivatives; Breast cancer; Pediococcus; Probiotics.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pediococcus acidilactici isolated from traditional cheese as a potential probiotic with cytotoxic activity against doxorubicin-resistant MCF-7 cells.3 Biotech. 2023 Jun;13(6):170. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03597-w. Epub 2023 May 9. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37188290 Free PMC article.
-
A Newly Characterized Potentially Probiotic Strain, Lactobacillus brevis MK05, and the Toxicity Effects of its Secretory Proteins Against MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2021 Aug;13(4):982-992. doi: 10.1007/s12602-021-09766-8. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2021. PMID: 33687634
-
Selection and characterization of probiotic lactic acid bacteria and its impact on growth, nutrient digestibility, health and antioxidant status in weaned piglets.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 8;13(3):e0192978. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192978. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29518093 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of non-starter lactic acid bacteria in autochthonous dairy products from Western Balkan Countries - Technological and probiotic properties.Food Res Int. 2020 Oct;136:109494. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109494. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Food Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32846575 Review.
-
Lacticaseibacillus paracasei LB12, a Potential Probiotic Isolated from Traditional Iranian Fermented Milk (Doogh).Curr Microbiol. 2023 Sep 2;80(10):333. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03376-z. Curr Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37658854 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory effects of probiotic Bacillus coagulans against MCF7 breast cancer cells.Iran J Microbiol. 2021 Dec;13(6):839-847. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v13i6.8089. Iran J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 35222863 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping the Physicochemical, Functional, Microbiological and Sensory Properties of Yoghurts Using Plant Additives.Foods. 2023 Mar 17;12(6):1275. doi: 10.3390/foods12061275. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36981201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-regulation of biofilm-associated genes in mecA-positive methicillin-resistant S. aureus treated with M. communis extract and its antibacterial activity.AMB Express. 2021 Jun 10;11(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13568-021-01247-z. AMB Express. 2021. PMID: 34110520 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Potential of Post-Fermentation Media and Cell Extracts of Probiotic Strains: An In Vitro Study.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 6;14(7):1853. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071853. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406625 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance in potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria of fermented foods and human origin from Nigeria.BMC Microbiol. 2023 May 19;23(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02883-0. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37208603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elfahri K.R., Vasiljevic T., Yeager T., Donkor O.N. Anti-colon cancer and antioxidant activities of bovine skim milk fermented by selected Lactobacillus helveticus strains. J. Dairy Sci. 2016;99:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Bray F., Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Siegel R.L., Torre L.A., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Wang S.-M., Zhang L.-W., Fan R.-B., Han X., Yi H.-X., Zhang L.-L., Xue C.-H., Li H.-B., Zhang Y.-H., Shigwedha N. Induction of HT-29 cells apoptosis by lactobacilli isolated from fermented products. Res. Microbiol. 2014;165:202–214. - PubMed
-
- Kahouli I., Malhotra M., Alaoui-Jamali M., Prakash S. In-vitro characterization of the anti-cancer activity of the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus fermentum NCIMB 5221 and potential against colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2015;7:224–235.
-
- Patel S. Breast cancer: lesser-known facets and hypotheses. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018;98:499–506. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
