Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay With Lateral Flow Dipstick Assay for Rapid Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus
- PMID: 33598439
- PMCID: PMC7882697
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.613304
Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay With Lateral Flow Dipstick Assay for Rapid Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus
Abstract
Background: The emerging Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) has challenged the public health globally. With the increasing requirement of detection for SARS-CoV-2 outside of the laboratory setting, a rapid and precise Point of Care Test (POCT) is urgently needed.
Methods: Targeting the nucleocapsid (N) gene of SARS-CoV-2, specific primers, and probes for reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification coupled with lateral flow dipstick (RT-RAA/LFD) platform were designed. For specificity evaluation, it was tested with human coronaviruses, human influenza A virus, influenza B viruses, respiratory syncytial virus, and hepatitis B virus, respectively. For sensitivity assay, it was estimated by templates of recombinant plasmid and pseudovirus of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. For clinical assessment, 100 clinical samples (13 positive and 87 negatives for SARS-CoV-2) were tested via quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR) and RT-RAA/LFD, respectively.
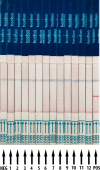
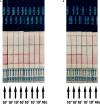
Results: The limit of detection was 1 copies/μl in RT-RAA/LFD assay, which could be conducted within 30 min at 39°C, without any cross-reaction with other human coronaviruses and clinical respiratory pathogens. Compared with RT-qPCR, the established POCT assay offered 100% specificity and 100% sensitivity in the detection of clinical samples.
Conclusion: This work provides a convenient POCT tool for rapid screening, diagnosis, and monitoring of suspected patients in SARS-CoV-2 endemic areas.
Keywords: Coronavirus Disease-2019; Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2; lateral flow dipstick; point of care test; reverse-transcription recombinase-aided amplification.
Copyright © 2021 Zheng, Chen, Li, Wu, Wen, Liu, Lin, Liang, Huang, Zha, Yang, Li, Zhong, Liu, Cheng, Song and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
Author L-JL was employed by the company Chaozhou Hybribio Limited Corporation, Chaozhou, Guangdong Province, People’s Republic of China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Behrmann O., Bachmann I., Spiegel M., Schramm M., El Wahed A. A., Dobler G., et al. (2020). Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 by low volume real-time single tube reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification using an exo probe with an internally linked quencher (exo-IQ). Clin. Chem. 66(8), 1047–1054 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa116 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- El-Tholoth M., Bau H. H., Song J. (2020). A Single and Two-Stage, Closed-Tube, Molecular Test for the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) at Home, Clinic, and Points of Entry. ChemRxiv [Preprint]. 10.26434/chemrxiv.11860137.v1 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

