Noninvasive Imaging in Interventional Cardiology: Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
- PMID: 33598485
- PMCID: PMC7882516
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.637838
Noninvasive Imaging in Interventional Cardiology: Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Abstract
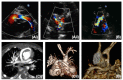
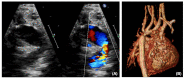
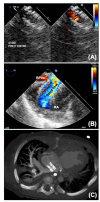
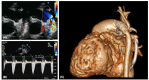
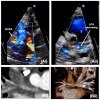
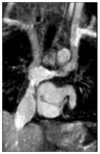
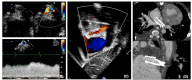
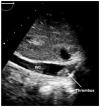
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a spectrum of left heart underdevelopment leaving the left side unable to support the systemic circulation. If active management is pursued, then the condition is managed with staged palliation to the Fontan circulation, leaving a systemic right ventricle. Through all surgical stages, and even after completion of Fontan, there are multiple areas that may require intervention, most frequently the branch pulmonary arteries which are essential to a successful Fontan circulation. Echocardiography is the mainstay of assessment, but there is an increasing use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) particularly in relation to extracardiac structures which can be more challenging with echocardiography. Both MRI and CT require set-up, experience and training, and usually sedation or anesthetic in smaller children, but can provide excellent imaging to guide interventions. Cardiac MRI is also able to quantify right ventricular (RV) function which can be challenging on echocardiography. This article describes the modalities available and their use in assessing patients with HLHS prior to catheter interventions.
Keywords: Fontan; Glenn; MRI; Norwood; computed tomography; echocardiography; hybrid; hypoplastic left heart syndrome.
Copyright © 2021 Bellsham-Revell.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Atz AM, Travison TG, Williams IA, Pearson GD, Laussen PC, Mahle WT, et al. . Prenatal diagnosis and risk factors for preoperative death in neonates with single right ventricle and systemic outflow obstruction: screening data from the Pediatric Heart Network Single Ventricle Reconstruction Trial(*). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2010) 140:1245–50. 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.05.022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

