Motivational Interviewing Training: A Case-Based Curriculum for Preclinical Medical Students
- PMID: 33598544
- PMCID: PMC7880250
- DOI: 10.15766/mep_2374-8265.11104
Motivational Interviewing Training: A Case-Based Curriculum for Preclinical Medical Students
Abstract
Introduction: With the rise of chronic medical problems involving lifestyle behaviors and the benefits of patient involvement in preventative care, medical students need to learn how to help patients change health risk behaviors and improve patient involvement in order to improve health outcomes. Motivational interviewing (MI) is a patient-centered therapeutic approach that is effective in the treatment of lifestyle behaviors and diseases.
Methods: This 2-hour didactic training session, along with a 3-hour case-based practice session involving role-plays and a 3-hour evaluated session utilizing standardized patients, was delivered to 68 preclinical medical students. Knowledge, attitudes, and self-efficacy were evaluated via pre- and posttraining surveys, and satisfaction with the training was assessed upon completion.
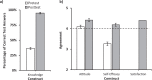
Results: Students who completed both pre- and postsurveys (n = 48) showed a statistically significant improvement in knowledge of MI (t = -29.73, df = 47, p < .001), attitudes regarding implementing MI in health care settings (t = -3.04, df = 47, p < .005), and self-efficacy (t = -10.699, df = 47, p < .001) in talking with patients about behavior change. Students were also highly satisfied with the MI training package (M of 4.4, SD = 0.6, out of 5.0).
Discussion: A training package to teach preclinical medical students about MI was effective in helping students learn the knowledge and skills necessary to deliver MI in a broad range of clinical cases.
Keywords: Communication Skills; Motivational Interviewing; Preventive Medicine.
© 2021 Jacobs et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence for motivational interviewing in educational settings among medical schools: a scoping review.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Aug 8;24(1):856. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05845-w. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39118104 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Implementation and Impact of a Motivational Interviewing Workshop on Medical Student Knowledge and Social Cognitions Towards Counseling Patients on Lifestyle Behaviors.Teach Learn Med. 2020 Apr-May;32(2):218-230. doi: 10.1080/10401334.2019.1681273. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Teach Learn Med. 2020. PMID: 31656080
-
Motivating residents to change communication: the role of a brief motivational interviewing didactic.Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2019 Aug 27;20:e124. doi: 10.1017/S146342361900015X. Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2019. PMID: 31451128 Free PMC article.
-
"A change would do you good": Training medical students in Motivational Interviewing using a blended-learning approach - A pilot evaluation.Patient Educ Couns. 2019 Apr;102(4):663-669. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2018.10.027. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Patient Educ Couns. 2019. PMID: 30448043
-
Teaching Motivational Interviewing to Medical Students: A Systematic Review.Acad Med. 2020 Mar;95(3):458-469. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000003011. Acad Med. 2020. PMID: 31577585
Cited by
-
Which patient and surgeon characteristics are associated with surgeon experience of stress during an office visit?PEC Innov. 2022 Apr 22;1:100043. doi: 10.1016/j.pecinn.2022.100043. eCollection 2022 Dec. PEC Innov. 2022. PMID: 37213725 Free PMC article.
-
Medical Nutrition Education for Health, Not Harm: BMI, Weight Stigma, Eating Disorders, and Social Determinants of Health.Med Sci Educ. 2024 Apr 2;34(3):679-690. doi: 10.1007/s40670-024-02025-9. eCollection 2024 Jun. Med Sci Educ. 2024. PMID: 38887425 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Interventions to Improve Pediatric Vaccine Uptake in Hesitant Cohorts: A Scoping Review.Cureus. 2025 May 19;17(5):e84399. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84399. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40535401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for motivational interviewing in educational settings among medical schools: a scoping review.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Aug 8;24(1):856. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05845-w. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39118104 Free PMC article.
-
Motivational Interviewing: Addressing Interest Among Health Professions Students.PRiMER. 2024 Jun 24;8:35. doi: 10.22454/PRiMER.2024.823357. eCollection 2024. PRiMER. 2024. PMID: 38946753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sahler OJZ, Carr JE, Frank JB, Nunes JV. The Behavioral Sciences and Health Care. 4th ed Hogrefe; 2018.
-
- Miller WR Motivational interviewing with problem drinkers. Behav Cogn Psychother. 1983;11(2):147–172. 10.1017/S0141347300006583 - DOI
-
- Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People to Change Addictive Behaviors. Guilford; 1991.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
