STudy of Antithrombotic Treatment after IntraCerebral Haemorrhage: Protocol for a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 33598560
- PMCID: PMC7856578
- DOI: 10.1177/2396987320954671
STudy of Antithrombotic Treatment after IntraCerebral Haemorrhage: Protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background and aims: Many patients with prior intracerebral haemorrhage have indications for antithrombotic treatment with antiplatelet or anticoagulant drugs for prevention of ischaemic events, but it is uncertain whether such treatment is beneficial after intracerebral haemorrhage. STudy of Antithrombotic Treatment after IntraCerebral Haemorrhage will assess (i) the effects of long-term antithrombotic treatment on the risk of recurrent intracerebral haemorrhage and occlusive vascular events after intracerebral haemorrhage and (ii) whether imaging findings, like cerebral microbleeds, modify these effects.
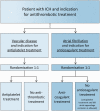
Methods: STudy of Antithrombotic Treatment after IntraCerebral Haemorrhage is a multicentre, randomised controlled, open trial of starting versus avoiding antithrombotic treatment after non-traumatic intracerebral haemorrhage, in patients with an indication for antithrombotic treatment. Participants with vascular disease as an indication for antiplatelet treatment are randomly allocated to antiplatelet treatment or no antithrombotic treatment. Participants with atrial fibrillation as an indication for anticoagulant treatment are randomly allocated to anticoagulant treatment or no anticoagulant treatment. Cerebral CT or MRI is performed before randomisation. Duration of follow-up is at least two years. The primary outcome is recurrent intracerebral haemorrhage. Secondary outcomes include occlusive vascular events and death. Assessment of clinical outcomes is performed blinded to treatment allocation. Target recruitment is 500 participants.Trial status: Recruitment to STudy of Antithrombotic Treatment after IntraCerebral Haemorrhage is on-going. On 30 April 2020, 44 participants had been enrolled in 31 participating hospitals. An individual patient-data meta-analysis is planned with similar randomised trials.
Keywords: Intracerebral haemorrhage; anticoagulant; antiplatelet; antithrombotic treatment; atrial fibrillation; ischaemic events; randomised controlled trial; secondary prevention; stroke.
© European Stroke Organisation 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: JP has served on a scientific advisory board for and received lecture fees from Bayer. CK has received lecture fees from Novo Nordic and Bristol-Myers Squibb Denmark. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
-
- Hart RG, Pearce LA, Aguilar MI. Meta-analysis: antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med 2007; 146: 857–867. - PubMed
-
- Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E, et al.. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2014; 383: 955–962. - PubMed
-
- van Asch CJ, Luitse MJ, Rinkel GJ, et al.. Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 2010; 9: 167–176. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous