Smell and Taste Impairment in a Nationwide Sample of US Adults With Chronic Rhinosinusitis Symptoms
- PMID: 33598596
- PMCID: PMC7863166
- DOI: 10.1177/2473974X20986756
Smell and Taste Impairment in a Nationwide Sample of US Adults With Chronic Rhinosinusitis Symptoms
Abstract
Objective: To estimate the prevalence of objectively confirmed olfactory and gustatory dysfunction in US adults reporting chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) symptoms in a nationally representative database.
Study design: Cross-sectional epidemiologic analysis.
Setting: Data were analyzed from the smell and taste component of the 2013-2014 NHANES data set (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey).
Methods: Individuals reporting the presence of ≥2 cardinal CRS symptoms (nasal blockage, sinus pain, discolored mucus, and dysosmia) were identified as patients with a potential diagnosis of CRS. Associations were examined between the presence of CRS symptoms and both self-reported and objectively measured smell and taste.
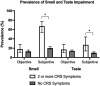
Results: One-third (33%) of adults who have ≥2 CRS symptoms report subjective olfactory impairment, though only 18% of these adults have quantifiable olfactory dysfunction on objective testing. Of these adults, 27% report subjective taste impairment, but just 17% have quantifiable gustatory dysfunction on objective testing. The presence of ≥2 CRS symptoms was not significantly associated with objective olfactory or gustatory dysfunction, although the individual symptoms of subjective dysosmia and discolored mucus were associated with objectively confirmed olfactory dysfunction.
Conclusion: The prevalence of objective olfactory and gustatory dysfunction was higher among adults reporting the presence of ≥2 CRS symptoms, but the differences were not statistically significant. Specific sinonasal symptoms, including discolored mucus and subjective smell dysfunction, were significantly associated with objective smell impairment.
Keywords: NHANES; chronic rhinosinusitis; hyposmia; olfaction; taste.
© The Authors 2021.
Figures
References
-
- Bhattacharyya N, Gilani S. Prevalence of potential adult chronic rhinosinusitis symptoms in the United States. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;159(3):522-525. doi:10.1177/019459981 8774006 - PubMed
-
- Pleis JR, Lethbridge-Cejku M. Summary health statistics for US adults: national health interview survey, 2006. Vital Health Stat 10 2007;(235):1-153. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources