Development of vaccine formulations: past, present, and future
- PMID: 33598818
- PMCID: PMC7889058
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-021-00924-7
Development of vaccine formulations: past, present, and future
Abstract
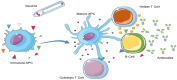
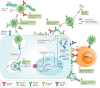
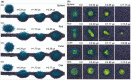
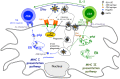
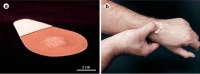
The current situation, heavily influenced by the ongoing pandemic, puts vaccines back into the spotlight. However, the conventional and traditional vaccines present disadvantages, particularly related to immunogenicity, stability, and storage of the final product. Often, such products require the maintenance of a "cold chain," impacting the costs, the availability, and the distribution of vaccines. Here, after a recall of the mode of action of vaccines and the types of vaccines currently available, we analyze the past, present, and future of vaccine formulation. The past focuses on conventional formulations, the present discusses the use of nanoparticles for vaccine delivery and as adjuvants, while the future presents microneedle patches as alternative formulation and administration route. Finally, we compare the advantages and disadvantages of injectable solutions, nanovaccines, and microneedles in terms of efficacy, stability, and patient-friendly design. Different approaches to vaccine formulation development, the conventional vaccine formulations from the past, the current development of lipid nanoparticles as vaccines, and the near future microneedles formulations are discussed in this review.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Immunotherapy; Microneedles; Nanoparticles; Vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

