Discovery of Cyanobacterial Natural Products Containing Fatty Acid Residues*
- PMID: 33599093
- PMCID: PMC8252387
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202015105
Discovery of Cyanobacterial Natural Products Containing Fatty Acid Residues*
Abstract
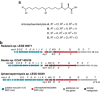
In recent years, extensive sequencing and annotation of bacterial genomes has revealed an unexpectedly large number of secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters whose products are yet to be discovered. For example, cyanobacterial genomes contain a variety of gene clusters that likely incorporate fatty acid derived moieties, but for most cases we lack the knowledge and tools to effectively predict or detect the encoded natural products. Here, we exploit the apparent absence of a functional β-oxidation pathway in cyanobacteria to achieve efficient stable-isotope-labeling of their fatty acid derived lipidome. We show that supplementation of cyanobacterial cultures with deuterated fatty acids can be used to easily detect natural product signatures in individual strains. The utility of this strategy is demonstrated in two cultured cyanobacteria by uncovering analogues of the multidrug-resistance reverting hapalosin, and novel, cytotoxic, lactylate-nocuolin A hybrids-the nocuolactylates.
Keywords: cyanobacteria; isotopic labeling; natural products discovery; oxadiazines; oxidation.
© 2021 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Hug J. J., Krug D., Müller R., Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 172–193. - PubMed
-
- Ziemert N., Alanjary M., Weber T., Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 988–1005. - PubMed
-
- van der Hooft J. J. J., Mohimani H., Bauermeister A., Dorrestein P. C., Duncan K. R., Medema M. H., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3297–3314. - PubMed
-
- Ramos A. E. F., Evanno L., Poupon E., Champy P., Beniddir M. A., Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 960–980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

