In Vitro Cultivation of the Syphilis Spirochete Treponema pallidum
- PMID: 33599121
- PMCID: PMC7986111
- DOI: 10.1002/cpz1.44
In Vitro Cultivation of the Syphilis Spirochete Treponema pallidum
Erratum in
-
Group Correction Statement (Data Availability Statements).Curr Protoc. 2022 Aug;2(8):e552. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.552. Curr Protoc. 2022. PMID: 36005902 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Group Correction Statement (Conflict of Interest Statements).Curr Protoc. 2022 Aug;2(8):e551. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.551. Curr Protoc. 2022. PMID: 36005903 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
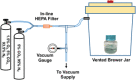
For over a century, investigation of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum, the spiral-shaped bacterium that causes syphilis, was hindered by an inability to culture the organism in vitro. A recent breakthrough has enabled continuous in vitro growth of this organism in co-culture with mammalian tissue culture cells. This article contains the protocols needed to culture T. pallidum in the standard laboratory environment. In addition, protocols for growing and maintaining the required tissue culture cells, for generating isogenic strains by limiting dilution, and for quantitating T. pallidum by darkfield microscopy are included. © 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC. Basic Protocol 1: In vitro cultivation of Treponema pallidum Basic Protocol 2: Generation of isogenic strains Support Protocol 1: Alternate harvest procedure Support Protocol 2: Culture of Sf1Ep cells Support Protocol 3: Assessment of T. pallidum number and viability.
Keywords: Treponema pallidum; cell culture; in vitro cultivation; laboratory growth; spirochetes; syphilis.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures

References
-
- Cumberland, M. C. , & Turner, T. B. (1949). The rate of multiplication of Treponema pallidum in normal and immune rabbits. American Journal of Syphilis, 33, 201–211. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

