Orthogonal Bioluminescent Probes from Disubstituted Luciferins
- PMID: 33599497
- PMCID: PMC7955686
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00894
Orthogonal Bioluminescent Probes from Disubstituted Luciferins
Abstract
Bioluminescence imaging with luciferase-luciferin pairs is routinely used to monitor cellular functions. Multiple targets can be visualized in tandem using luciferases that process unique substrates, but only a handful of such orthogonal probes are known. Multiplexed studies require additional robust, light-emitting molecules. In this work, we report new luciferins for orthogonal imaging that comprise disubstituted cores. These probes were found to be bright emitters with various engineered luciferases. The unique patterns of light output also provided insight into enzyme-substrate interactions necessary for productive emission. Screening studies identified mutant luciferases that could preferentially process the disubstituted analogues, enabling orthogonal imaging with existing bioluminescent reporters. Further mutational analyses revealed the origins of substrate selectivity. Collectively, this work provides insights into luciferase-luciferin features relevant to bioluminescence and expands the number of probes for multicomponent tracking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
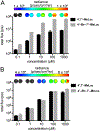
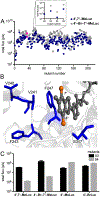
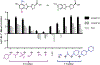
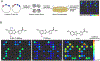
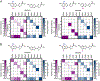
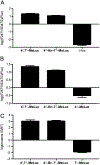

References
-
- Prescher JA, Contag CH (2010) Guided by the light: visualizing biomolecular processes in living animals with bioluminescence, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 14, 80–89. - PubMed
-
- Contag CH, Spilman SD, Contag PR, Oshiro M, Eames B, Dennery P, Stevenson DK, Benaron DA . (1997) Visualizing gene expression in living mammals using a bioluminescent reporter, Photochem. Photobiol 66, 523–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

