Dorsal and ventral mossy cells differ in their axonal projections throughout the dentate gyrus of the mouse hippocampus
- PMID: 33600026
- PMCID: PMC8247909
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.23314
Dorsal and ventral mossy cells differ in their axonal projections throughout the dentate gyrus of the mouse hippocampus
Abstract
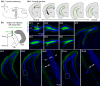
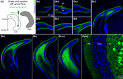
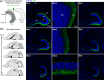
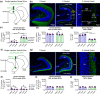
Glutamatergic hilar mossy cells (MCs) have axons that terminate both near and far from their cell body but stay within the DG, making synapses primarily in the molecular layer. The long-range axons are considered the primary projection, and extend throughout the DG ipsilateral to the soma, and project to the contralateral DG. The specificity of MC axons for the inner molecular layer (IML) has been considered to be a key characteristic of the DG. In the present study, we made the surprising finding that dorsal MC axons are an exception to this rule. We used two mouse lines that allow for Cre-dependent viral labeling of MCs and their axons: dopamine receptor D2 (Drd2-Cre) and calcitonin receptor-like receptor (Crlr-Cre). A single viral injection into the dorsal DG to label dorsal MCs resulted in labeling of MC axons in both the IML and middle molecular layer (MML). Interestingly, this broad termination of dorsal MC axons occurred throughout the septotemporal DG. In contrast, long-range axons of ventral MCs terminated in the IML, consistent with the literature. Taken together, these results suggest that dorsal and ventral MCs differ significantly in their axonal projections. Since MC projections in the ML are thought to terminate primarily on GCs, the results suggest a dorsal-ventral difference in MC activation of GCs. The surprising difference in dorsal and ventral MC projections should therefore be considered when evaluating dorsal-ventral differences in DG function.
Keywords: GABA; axon; commissural; hilus; long-range; molecular layer; virus.
© 2021 The Authors. Hippocampus published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial interests that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Azevedo, E. P. , Pomeranz, L. , Cheng, J. , Schneeberger, M. , Vaughan, R. , Stern, S. A. , … Friedman, J. M. (2019). A role of Drd2 hippocampal neurons in context‐dependent food intake. Neuron, 102, 873–886.e875. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, H. L. , Lu, Y. L. , Botterill, J. J. , Duffy, A. M. , LaFrancois, J. , & Scharfman, H. (2020). Excitatory effects of dentate gyrus mossy cells and their ability to influence granule cell firing: an optogenetic study in adult mouse hippocampal slices. bioRxiv, 1–105. 10.1101/2020.06.06.137844 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

