Analysis of Asymptomatic and Presymptomatic Transmission in SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak, Germany, 2020
- PMID: 33600301
- PMCID: PMC8007320
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2704.204576
Analysis of Asymptomatic and Presymptomatic Transmission in SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak, Germany, 2020
Abstract
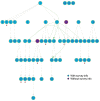
We determined secondary attack rates (SAR) among close contacts of 59 asymptomatic and symptomatic coronavirus disease case-patients by presymptomatic and symptomatic exposure. We observed no transmission from asymptomatic case-patients and highest SAR through presymptomatic exposure. Rapid quarantine of close contacts with or without symptoms is needed to prevent presymptomatic transmission.
Keywords: COVID-19; Germany; SARS-CoV-2; asymptomatic diseases; contact; coronavirus disease; disease transmission; epidemiology; infectious; respiratory infections; risk; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- Huang L, Zhang X, Zhang X, Wei Z, Zhang L, Xu J, et al. Rapid asymptomatic transmission of COVID-19 during the incubation period demonstrating strong infectivity in a cluster of youngsters aged 16-23 years outside Wuhan and characteristics of young patients with COVID-19: A prospective contact-tracing study. J Infect. 2020;80:e1–13. 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

