Imbalance of TGF-β1/BMP-7 pathways induced by M2-polarized macrophages promotes hepatocellular carcinoma aggressiveness
- PMID: 33601054
- PMCID: PMC8178441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.02.016
Imbalance of TGF-β1/BMP-7 pathways induced by M2-polarized macrophages promotes hepatocellular carcinoma aggressiveness
Abstract
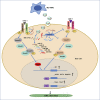
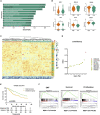
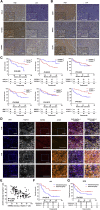
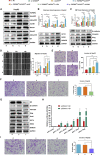
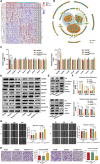
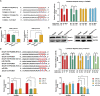
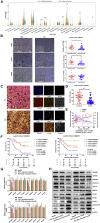
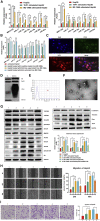
The transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway is the predominant cytokine signaling pathway in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), another member of the TGF-β superfamily, has been frequently found to participate in crosstalk with the TGF-β pathway. However, the complex interaction between the TGF-β and BMP pathways has not been fully elucidated in HCC. We found that the imbalance of TGF-β1/BMP-7 pathways was associated with aggressive pathological features and poor clinical outcomes in HCC. The induction of the imbalance of TGF-β1/BMP-7 pathways in HCC cells could significantly promote HCC cell invasion and stemness by increasing inhibitor of differentiation 1 (ID1) expression. We also found that the microRNA (miR)-17-92 cluster, originating from the extracellular vesicles (EVs) of M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages (M2-TAMs), stimulated the imbalance of TGF-β1/BMP-7 pathways in HCC cells by inducing TGF-β type II receptor (TGFBR2) post-transcriptional silencing and inhibiting activin A receptor type 1 (ACVR1) post-translational ubiquitylation by targeting Smad ubiquitylation regulatory factor 1 (Smurf1). In vivo, short hairpin (sh)-MIR17HG and ACVR1 inhibitors profoundly attenuated HCC cell growth and metastasis by rectifying the imbalance of TGF-β1/BMP-7 pathways. Therefore, we proposed that the imbalance of TGF-β1/BMP-7 pathways is a feasible prognostic biomarker and recovering the imbalance of TGF-β1/BMP-7 pathways might be a potential therapeutic strategy for HCC.
Copyright © 2021 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F., Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Siegel R.L., Torre L.A., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Ling C.Q., Fan J., Lin H.S., Shen F., Xu Z.Y., Lin L.Z., Qin S.K., Zhou W.P., Zhai X.F., Li B., Zhou Q.H., Chinese Integrative Therapy of Primary Liver Cancer Working Group Clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of primary liver cancer with integrative traditional Chinese and Western medicine. J. Integr. Med. 2018;16:236–248. - PubMed
-
- Zhao H.T., Meng Y.B., Zhai X.F., Cheng B.B., Yu S.S., Yao M., Yin H.X., Wan X.Y., Yang Y.K., Liu H. Comparable effects of Jiedu Granule, a compound Chinese herbal medicine, and sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective multicenter cohort study. J. Integr. Med. 2020;18:319–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

