Vulvar Aphthous Ulcer in an Adolescent With COVID-19
- PMID: 33601070
- PMCID: PMC7883736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpag.2021.02.098
Vulvar Aphthous Ulcer in an Adolescent With COVID-19
Abstract
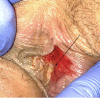
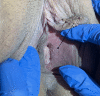
Background: Vulvar aphthous ulcers have been associated with various prodromal viral illnesses. We describe the case of an adolescent girl who developed vulvar aphthous ulcers during infection with Coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2.
Case: A 19-year-old girl presented to the emergency department with cough, sore throat, fevers, and rash, and tested positive for COVID-19. She re-presented 2 days later with vulvar pain and was found to have a vulvar aphthous ulcer. She was admitted for pain control and treated with oral steroids. Improvement in her vulvar pain was noted, along with resolution of fevers, cough, and rash.
Summary and conclusion: This case illustrates the novel association of COVID-19 with vulvar aphthous ulcers in adolescents. Use of oral steroids for symptomatic management of COVID-19 led to rapid clinical improvement.
Keywords: COVID-19; clinical presentation; vulvar aphthous ulcers.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Farhi D., Wendling J., Molinari E., et al. Non–sexually related acute genital ulcers in 13 pubertal girls: a clinical and microbiological study. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:38. - PubMed
-
- Lehman J., Bruce A., Wetter D., et al. Reactive nonsexually related acute genital ulcers: review of cases evaluated at Mayo Clinic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:44. - PubMed
-
- Farag Ahmed E.S. Nonsexually acquired acute genital ulceration: a commonly misdiagnosed condition. Gulf J Dermatol Venereol. 2018;25:13.
-
- Dixit S., Bradford J., Fischer G. Management of nonsexually acquired genital ulceration using oral and topical corticosteroids followed by doxycycline prophylaxis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous