Age moderated-anxiety mediation for multimodal treatment outcome among children with obsessive-compulsive disorder: An evaluation with correspondence analysis
- PMID: 33601717
- PMCID: PMC9555304
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.12.198
Age moderated-anxiety mediation for multimodal treatment outcome among children with obsessive-compulsive disorder: An evaluation with correspondence analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Anxiety expression varies by age in youth, and evaluation of putative mechanisms in treatment must consider both conjointly. Accordingly, age would moderate the mediation effect of anxiety in a youth obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) treatment trial.
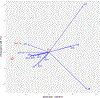
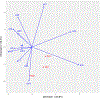
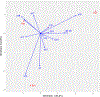
Methods: Fifty-six children ages 7 - 17 participated in an RCT comparing three treatments: CBT with standard dosing of sertraline, CBT with slow dosing of sertraline, and CBT with placebo. To examine the moderated-mediation effects for OCD symptom improvement, we discretized the continuous anxiety and OCD measures into three symptom outcome categories, "improved", "unchanged", and "deteriorated". To evaluate the moderating effect of age, we further examined the association of age and anxiety with the "improved" OCD category. For analysis, the age groups used as rows were cross tabulated with discretized anxiety and OCD measures. To estimate category associations with correlations, we adopted correspondence analysis.
Results: The correlational results indicate that for all treatment conditions, age was a moderator of the mediation effect of physical anxiety symptoms for the improved OCD measures (outcomes). Specifically, age suppressed correlations with OCD outcomes, with Physical Symptoms as a mediator for the outcome measures. This moderated mediation effect was most evident for ages 8-10 in the CBT with placebo group.
Limitations: The moderated mediation effect manifest in this single RCT-based study should be validated in other studies.
Discussion: Future research investigating a wider range of ages as a potential moderator of other symptom and emotion mediators of outcome is warranted, particularly in relation to individual symptom profiles of OCD.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest:
We have no known conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Allison DB, Allison RL, Faith MS, Paultre F, Pi-Sunyer FX (2007). Power and money: Designing statistically powerful studies while minimizing financial costs. Psychological Methods, 2, 20–33.
-
- Areán PA, & Kraemer HC (2013). High-quality psychotherapy research: From conception to piloting to national trials. New York: Oxford University Press.
-
- Baldwin DS, Anderson IM, Nutt DJ, Allgulander C, Bandelow B, den Boer JA, Christman DM., … , & Wittchen HU. (2014). Evidence-based pharmacological treatment of anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder: A revision of the 2005 guidelines from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 28, 1–37. - PubMed
-
- Baron RM, & Kenny DA (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Beh EJ & Lombardo R.(2014). Correspondence Analysis: Theory, Practice and New Strategies. West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. doi: 10.1002/9781118762875. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

