Assessment of heterosis based on parental genetic distance estimated with SSR and SNP markers in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)
- PMID: 33602146
- PMCID: PMC7891138
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-021-07431-6
Assessment of heterosis based on parental genetic distance estimated with SSR and SNP markers in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)
Abstract
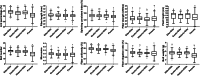
Background: Heterosis has been extensively utilized in different crops and made a significant contribution to global food security. Genetic distance (GD) is one of the valuable criteria for selecting parents in hybrid breeding. The objectives of this study were to estimate the GD between parents using both simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers and to investigate the efficiency of the prediction of hybrid performance based on GD. The experiment comprised of four male parents, 282 female parents and 1128 F1, derived from NCII mating scheme. The hybrids, their parents and two check cultivars were evaluated for two years. Performance of F1, mid-parent heterosis (MPH), and best parent heterosis (BPH) were evaluated for ten agronomic and fiber quality traits, including plant height, boll weight, boll number, lint percentage, fiber length, fiber strength, fiber uniformity, fiber elongation ratio, micronaire, and spinning consistent index.
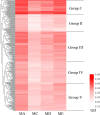
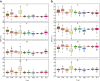
Results: Heterosis was observed in all hybrids and, the traits like plant height, boll number, boll weight and lint percentage exhibited higher heterosis than the fiber quality traits. Correlations were significant between parental and F1 performances. The F1 performances between three hybrid sets (Elite×Elite, Exotic×Elite, and Historic×Elite) showed significant differences in eight traits, including boll number, lint percentage, fiber length, fiber strength, fiber uniformity, fiber elongation ratio, micronaire, and spinning consistent index. The correlation of the GD assessed by both SSR and SNP markers was significantly positive. The cluster analysis based on GD results estimated using SNP showed that all the female parents divided into five groups and the F1 performance between these five groups showed significant differences in four traits, including lint percentage, micronaire, fiber strength, and fiber elongation ratio. The correlation between GD and F1 performance, MPH and BPH were significant for lint percentage and micronaire.
Conclusions: Our results suggested that GD between parents could be helpful in heterosis prediction for certain traits. This study reveals that molecular marker analysis can serve as a basis for assigning germplasm into heterotic groups and to provide guidelines for parental selection in hybrid cotton breeding.
Keywords: Genetic distance; Heterosis; SNP; SSR; Upland cotton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Heterosis and correlation in interspecific and intraspecific hybrids of cotton.Genet Mol Res. 2016 Jun 24;15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15028083. Genet Mol Res. 2016. PMID: 27420964
-
Combining ability analysis for within-boll yield components in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.).Genet Mol Res. 2012 Aug 24;11(3):2790-800. doi: 10.4238/2012.August.24.4. Genet Mol Res. 2012. PMID: 23007974
-
Association mapping analysis of fiber yield and quality traits in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.).Mol Genet Genomics. 2017 Dec;292(6):1267-1280. doi: 10.1007/s00438-017-1346-9. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Mol Genet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28748394
-
Unlocking the mystery of heterosis opens the era of intelligent rice breeding.Plant Physiol. 2024 Oct 1;196(2):735-744. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae385. Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39115386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Heterosis and Its Applications in Tree Breeding: Progress and Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 17;25(22):12344. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212344. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596408 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Estimating the combining ability and genetic parameters for growth habit, yield, and fiber quality traits in some Egyptian cotton crosses.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Mar 2;23(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04131-z. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 36859186 Free PMC article.
-
One Hundred Years of Progress and Pitfalls: Maximising Heterosis through Increasing Multi-Locus Nuclear Heterozygosity.Biology (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;13(10):817. doi: 10.3390/biology13100817. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on the Genetic Diversity Characteristics of the Endemic Plant Rhododendron bailiense in Guizhou, China Based on SNP Molecular Markers.Ecol Evol. 2025 Feb 8;15(2):e70966. doi: 10.1002/ece3.70966. eCollection 2025 Feb. Ecol Evol. 2025. PMID: 39926301 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between Parental Transcriptome and Field Data for the Characterization of Heterosis in Chinese Cabbage.Genes (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;14(4):776. doi: 10.3390/genes14040776. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107533 Free PMC article.
-
Inheritance, QTLs, and Candidate Genes of Lint Percentage in Upland Cotton.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 31;13:855574. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.855574. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35450216 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shull GH. The composition of a field of maize. J Heredity. 1908, os-4(1):296–301.
-
- Tang F, Xiao W. Genetic effects and heterosis of within-boll yield components in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Euphytica. 2013;194(1):41–51. doi: 10.1007/s10681-013-0958-3. - DOI
-
- Gowda M, Kling C, Würschum T, Liu W, Maurer HP, Hahn V, Reif JC. Hybrid breeding in durum wheat: heterosis and combining ability. Crop Sci. 2010;50(6):2224–2230. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2009.10.0637. - DOI
-
- Reif JC, Zhao Y, Würschum T, Gowda M, Hahn V, Léon J. Genomic prediction of sunflower hybrid performance. Plant Breed. 2013;132(1):107–114. doi: 10.1111/pbr.12007. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

