Evolutionary and structural analysis elucidates mutations on SARS-CoV2 spike protein with altered human ACE2 binding affinity
- PMID: 33602511
- PMCID: PMC7883683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.01.035
Evolutionary and structural analysis elucidates mutations on SARS-CoV2 spike protein with altered human ACE2 binding affinity
Abstract
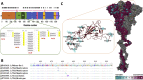
The recognition of ACE2 by the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of spike protein mediates host cell entry. The objective of the work is to identify SARS-CoV2 spike variants that emerged during the pandemic and evaluate their binding affinity with ACE2. Evolutionary analysis of 2178 SARS-CoV2 genomes identifies RBD variants that are under selection bias. The binding efficacy of these RBD variants to the ACE2 has been analyzed by using protein-protein docking and binding free energy calculations. Pan-proteomic analysis reveals 113 mutations among them 33 are parsimonious. Evolutionary analysis reveals five RBD variants A348T, V367F, G476S, V483A, and S494P are under strong positive selection bias. Variations at these sites alter the ACE2 binding affinity. A348T, G476S, and V483A variants display reduced affinity to ACE2 in comparison to the Wuhan SARS-CoV2 spike protein. While the V367F and S494P population variants display a higher binding affinity towards human ACE2. Reorientation of several crucial residues at the RBD-ACE2 interface facilitates additional hydrogen bond formation for the V367F variant which enhances the binding energy during ACE2 recognition. On the other hand, the enhanced binding affinity of S494P is attributed to strong interfacial complementarity between the RBD and ACE2.
Keywords: ACE2; Binding free energy; Population variants; Selection; Spike glycoprotein.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evolutionary and structural analysis elucidates mutations on SARS-CoV2 spike protein with altered human ACE2 binding affinity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 1;534:374-380. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.075. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33272568 Free PMC article.
-
V367F Mutation in SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Emerging during the Early Transmission Phase Enhances Viral Infectivity through Increased Human ACE2 Receptor Binding Affinity.J Virol. 2021 Jul 26;95(16):e0061721. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00617-21. Epub 2021 Jul 26. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34105996 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of common mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD and its ligand, the human ACE2 receptor on binding affinity and kinetics.Elife. 2021 Aug 26;10:e70658. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70658. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34435953 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain and their delicate balance between ACE2 affinity and antibody evasion.Protein Cell. 2024 May 28;15(6):403-418. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwae007. Protein Cell. 2024. PMID: 38442025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of S-protein RBD and hACE2 Interaction for Control of SARSCoV- 2 Infection (COVID-19).Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(6):689-703. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666201117111259. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33208074 Review.
Cited by
-
Screening of potential spike glycoprotein / ACE2 dual antagonists against COVID-19 in silico molecular docking.J Virol Methods. 2022 Mar;301:114424. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114424. Epub 2021 Dec 10. J Virol Methods. 2022. PMID: 34896453 Free PMC article.
-
Lower Gene Expression of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 Receptor in Lung Tissues of Smokers with COVID-19 Pneumonia.Biomolecules. 2021 May 26;11(6):796. doi: 10.3390/biom11060796. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34073591 Free PMC article.
-
De novo design of a stapled peptide targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor-binding domain.RSC Med Chem. 2023 Jul 31;14(9):1722-1733. doi: 10.1039/d3md00222e. eCollection 2023 Sep 19. RSC Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37731704 Free PMC article.
-
Alamandine: Potential Protective Effects in SARS-CoV-2 Patients.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2021 Nov 8;2021:6824259. doi: 10.1155/2021/6824259. eCollection 2021. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2021. PMID: 34853605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting Natural Evolution in the RBD Region of the Spike Glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 by Machine Learning.Viruses. 2024 Mar 20;16(3):477. doi: 10.3390/v16030477. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan J.F.-W., Kok K.-H., Zhu Z., Chu H., To K.K.-W., Yuan S., Yuen K.-Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan, Emerg. Microb. Infect. 2020;9:221–236. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

